About Time Gating (Time)
Time gating isolates a portion of a time record for further viewing and analysis. Time gating is often used to analyze non-stationary signals or portions of stationary signals such as burst signals from devices such as videotape recorders, computer disk drives, TDMA Time Division Multiple Access: A technology for digital transmission of radio signals between, for example, a mobile telephone and a radio base station. In TDMA, the frequency band is split into a number of channels which in turn are stacked into short time units so that several calls can share a single channel without interfering with one another. Networks using TDMA assign 6 timeslots for each frequency channel. TDMA is also the name of a digital technology based on the IS-136 standard. TDMA is the current designation for what was formerly known as D-AMPS. communication bursts, or ultrasonic transducers.
Time gating can only be used with and measurement types. However, most demodulators provide a way of selecting what part of the time capture to analyze. See topics for the tab in the dialog box for a particular demodulator. Also see Understanding Time and Frequency parameters.
The following illustration shows how time gating works. The time waveform on the left shows time-gating applied to the main time-record. The top waveform on the right shows the spectrum of the main time-record, and the third window shows the spectrum for the gated portion of the main time-record.
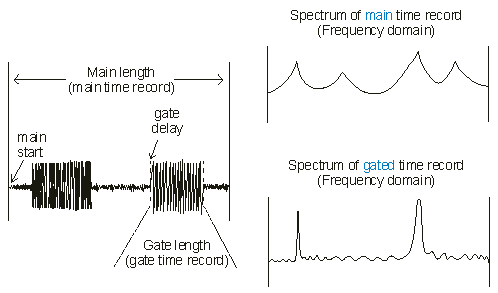
Time gating specifies a portion of the main time-record to be used for the following traces: spectrum, CCDF, CDF, PDF, frequency response, coherence, impulse response, autocorrelation, and cross correlation trace data.
When time gating is enabled, the VSA adds the word "Gate" to the trace title to indicate that the trace is computed from the gate time-record.
You can view the gate time-record with the Gate Time trace.
See Also
