Other topics about Fixture Simulator
The Fixture Simulator is a function that uses software in the E5071C to simulate various measurement conditions based on the measurement results. The functions available in Fixture Simulator are as follows:
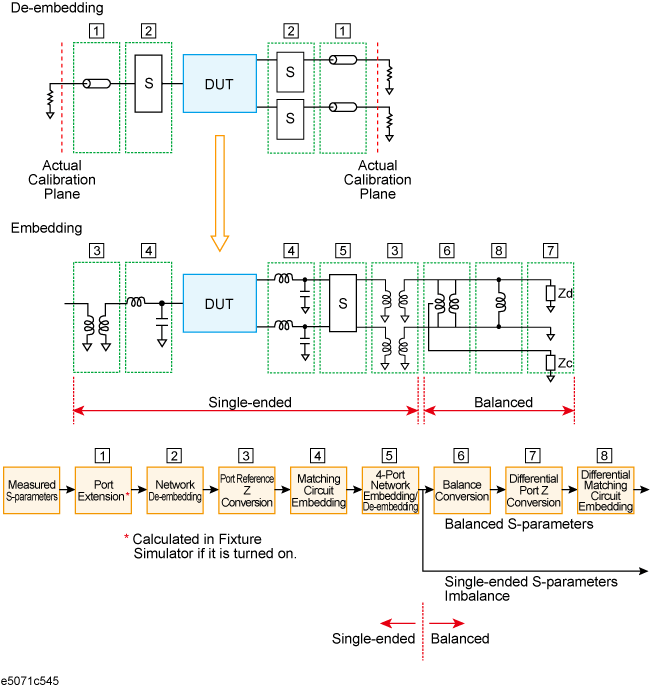
Data processing flow diagram of fixture simulator

Port extension is an independent function from the fixture simulator, but if the fixture simulator function is on, data processing is automatically executed as a function of the fixture simulator to improve the data processing efficiency. (Measurement result is the same as when the fixture simulator is turned off.) Port extension moves the calibration reference location by setting an electrical delay for a single-ended port. Port extension can eliminate only electrical delay (phase shift) for each single-ended port. Loss or mismatch cannot be eliminated by this function.
The following three functions are applied to single-ended ports (unbalanced ports). Balance-unbalance conversion can additionally be applied to single-ended ports.
A function that uses software to remove an arbitrary network (50 ohm system) defined by a two-port Touchstone data file from each test port (single-ended) and to extend the calibration plane. This makes it possible to remove networks that create error elements between the calibration plane and the DUT, thereby enabling a more realistic evaluation of the DUT.
For the setup procedure of the network de-embedding function, see Extending the Calibration Plane Using Network De-embedding.
A function that uses software to convert an S-parameter measured with a 50 ohm port reference impedance into a value measured with an arbitrary impedance.
For the setup procedure of port reference impedance conversion, see Converting the Port Impedance of the Measurement Result.
A function for converting an original measurement result into a characteristic determined under the condition of inserting a matching circuit between the DUT and the test port (single-ended). The matching circuit to be inserted is either selected from the five predetermined circuit models or provided by a designated arbitrary circuit defined in a two-port Touchstone file.
For the setup procedure used for matching circuit embedding, see Determining Characteristics After Adding a Matching Circuit.
This is a feature to embed (in terms of numerical calculation) your desired network that you have defined in a 4-port Touchstone data file into measurement results or to de-embed it from them.
When you use this as de-embedding, the embedded matching circuit and a part of networks in the DUT are removed.
For information on how to operate this function, refer to Obtaining Characteristics After Embedding/De-embedding 4-port Network.
When the 4-port network embedding/de-embedding feature reads a 4-port Touchstone data file, it does not automatically convert the file's normalized impedance value to adapt to the port reference impedance setting value of the analyzer.
A function that uses software to convert the measurement results in an unbalanced DUT state, which are obtained by connecting the DUT to the test port of the E5071C, into measurement results in a balanced state. Two test ports of the E5071C are connected to one balanced port of the DUT.
For the setup procedure used for balance-unbalance conversion, see Evaluating Balanced Devices (balance-unbalance conversion function).
The following two functions are applied to a balanced (differential) port converted by balance-unbalance conversion.
A function for converting the differential mode port impedance of a balanced port after an balance-unbalance conversion. Balance-unbalance conversion automatically converts the differential mode port impedance at the balanced port into 2Z0 and the common mode port impedance into Z0/2, compared with the two pre-conversion port impedances of Z0. Differential port impedance conversion further converts a differential port impedance after balance-unbalance conversion into an arbitrary port impedance.
For the setup procedure used for differential port impedance conversion, see Converting Reference Impedance of Balanced Port.
A function for converting the measurement results obtained from balance-unbalance conversion into a characteristic under the condition of inserting a matching circuit in the balanced port.
For setup procedure of differential matching circuit embedding, see Determining the Characteristics that Result from Adding a Matching Circuit to a Differential Port.