How ResBW Interacts With Other Parameters
The resolution bandwidth (ResBW or RBW Resolution Band Width (RBW or ResBW): specifies the minimum frequency bandwith that two separate frequency spectra can be resolved and viewed seperately. For FFT (digital) based VSA's the process is equivalent to passing a time-domain signal through a bank of bandpass filters, whose center frequencies correspond to the frequencies of the FFT bins. For a traditional swept-tuned (non-digital) spectrum analyzer, the resolution bandwidth is the bandwidth of the IF filter which determines the selectivity.) of spectrum traces depends on the window type and the time length (main time length, gate time length, or trace length for digital demods).
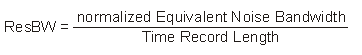
The normalized ENBW (equivalent noise bandwidth) is a constant that is determined by the selected Window Type.
One parameter that limits the minimum and maximum ResBW is span. Normally, the VSA automatically adjusts ResBW as you choose different frequency spans. However, you can select fixed RBW coupling to keep ResBW constant (fixed) as you change the frequency span.
The "DATA?" indicator will be present on a trace when ResBW is greater than span * 0.043. For details, see DATA?.
Normalized ENBW
Equivalent noise bandwidth (ENBW) is used to compare a window to the ideal, rectangular window of the same time length. ENBW is the bandwidth of a rectangular window ResBW filter that passes the same amount of energy as the ResBW filter defined by the window. For more information, see Window Shapefactor and Equivalent Noise BW.
The VSA defines resolution bandwidth (ResBW) as the Equivalent Noise Bandwidth of the selected time window.
Time Record Length
Time-record length and resolution bandwidth are inversely proportional, as shown in the ResBW equation shown previously. Changing Main Time Length changes and vice-versa. When is changed, the VSA automatically sets ResBW Mode to and ResBW Coupling to to allow arbitrary values to be specified for .
When Time Gating is enabled, depends on the gate instead of . In this case, changing gate length changes and vice-versa.
See Also
