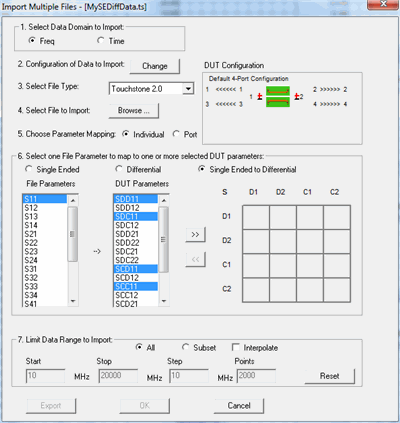
Build a single DUT file by importing data from multiple files
. The imported data are mapped to various parameters or ports.
The subsequent data can then be exported or analyzed by PLTS.
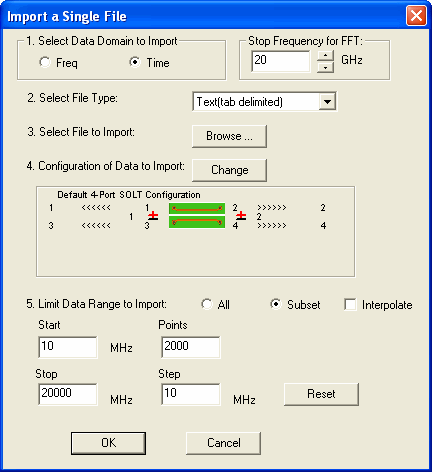
1. Select Data Domain to Import:
Frequency or Time. If
Time is selected, also type the Stop Frequency to be used in the
Fast Fourier Transform algorithm. 20 GHz is the default value,
and is best for most applications.
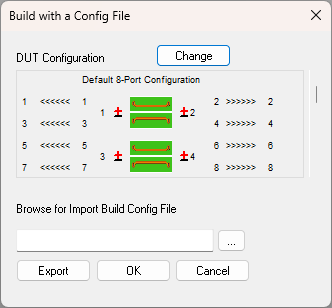
2. Configuration of Data to
Import (Build). Click
Change to launch the DUT
configuration dialog. These changes are reflected in the
DUT Configuration diagram in
the upper-right corner of the dialog.
Important
Note:
The DUT Configuration Change
and resulting picture does NOT
map the data as it is imported.
The DUT Configuration diagram in the upper-right corner
of the dialog does the following:
Shows the number of ports of the DUT
to be built. Shows how PLTS will perform the differential
math. Documents the DUT configuration as
you intend it to be built.
Use Step 5. and Step
6. to map the parameter data and ports. |
3.
Select File Type: Click the down-arrow to import
one of the following:
4.
Select File to Import: Click Browse to find the file
to import.
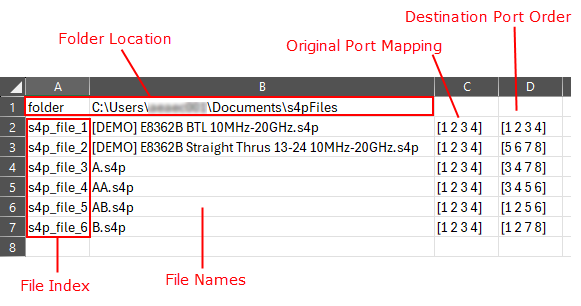
5. Choose Parameter Mapping:
In the following field, choose to map either Individual
parameters or Ports.
Note: To
perform NO re-mapping, select Port,
then click >> to
retain the original port mapping.
6.
Select one file parameter to map to one or more selected
DUT parameters.
This setting allows you to re-map
the imported data to alternate DUT ports.
Choose from:
Single-Ended
- Map Single-Ended file parameters to Single-Ended DUT
parameters. Differential
- Map Differential file parameters to Differential DUT
parameters. Single-Ended
to Differential
- Map Single-Ended file parameters to Differential DUT
parameters.
Choose a parameter in the left column (imported
data) to be remapped. Choose a parameter or port in the right column. Click >>
to make the change.
7.
Limit Data Range to Import:
All
- Import all of the available data. Subset
The following settings define the subset. Some settings
may require you to first check Interpolate.
Start
Lowest frequency or time of the data to import. Stop
Highest frequency or time of the data to import. Points
Number of data points measured from Start to Stop
frequency. Step
Frequency or time range between each data point;
available ONLY with Linear Spacing. Interpolate
May be checked automatically by PLTS if a subset setting
is made that requires Interpolation. Interpolated data is
not as accurate as measured data.
Checked - Subset settings have been changed
that require the imported data to be interpolated. Cleared - Imported data is NOT interpolated.
When Linear Spacing is selected, PLTS will change Subset
settings that you enter to the closest measured data values
which do not require interpolation. When Log, Dec, or
Oct Spacing is selected, PLTS may not allow Interpolate
to be cleared after changing settings. Click Reset to
return to the original values. Reset
Returns the Subset settings to the original values.
Export (Optional)
Click to export the remapped data.
Click OK to close the
dialog. |