Example 1. Hello World
This example shows how a user measurement's XML file, Python script, and FlexDCA's User Measurement Setup dialog relate to each other. This script does not perform a user measurement but does return a fictitious measurement (4.2) as required by FlexDCA.
This is a typical "Hello World" user measurement script which doesn't even make a measurement. It is designed to prove that your FlexDCA / Python environment is working correctly. After you've been successful with this example, try Example 2. Show Input Variables. Like all user-measurement Python scripts, HelloWorldScope.py consists of the following items:
- A function named algorithm. Your scripts can have additional functions, but it must have the algorithm function.
- FlexDCA passes a dictionary of input variables to the algorithm function.
- The script must return a dictionary of measurement results. These are the values that are returned to FlexDCA and get displayed in FlexDCA's measurement results table and indicate the measurement's status.
- If the measurement cannot be made, return a dictionary that has two keys "Status" with the value "Invalid" and "ErrorMsg" with the value that is an ASCII error string that you want displayed.
Because this script does not use the source waveform input variable, which is a NumPy array, NumPy does not need to be imported into the script.
The algorithm function name must be written in lower case. Naming the function Algorithm.m or ALGORITHM, for example, will break the script.
Do not use spaces or hyphens when selecting a file name for your script.
Procedure
- Make sure that you have properly installed Python.
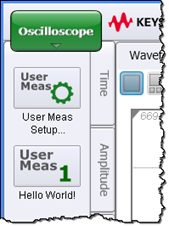
- Copy the following XML listing into a text editor. Name the file HelloWorldScope.xml and save it in any folder. For example, \Documents\Keysight\FlexDCA\User Measurements. Later, when this XML file is imported into the User Measurement Setup dialog, it identifies the HelloWorldScope.py script, populates the dialog, and creates the user measurement button as shown in these figures.
- Start your Python editor and enter the following script. Name your script file HelloWorldScope.py. In the script notice that:
- The SrcData key is passed to the variables dictionary to obtain the input waveform.
- The output variable,
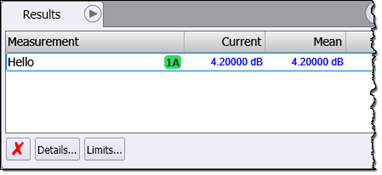
Result, returns a pretend measurement value, 4.2, to display on FlexDCA's Results table. This is a very simple script that doesn't even calculate a result. - Four variables are returned as a dictionary (key:value pairs).
- Place FlexDCA into Oscilloscope mode and display a single waveform on the display.
- In FlexDCA's User measurement tab, click the User Meas Setup button.
- In the dialog, select an available tab.
- Click Browse and select your XML configuration file, HelloWorld.xml.
- Close the dialog and click on your new Hello World! measurement button.
- In the Results panel, notice that the Hello World! measurement result of 4.2 dB is reported.
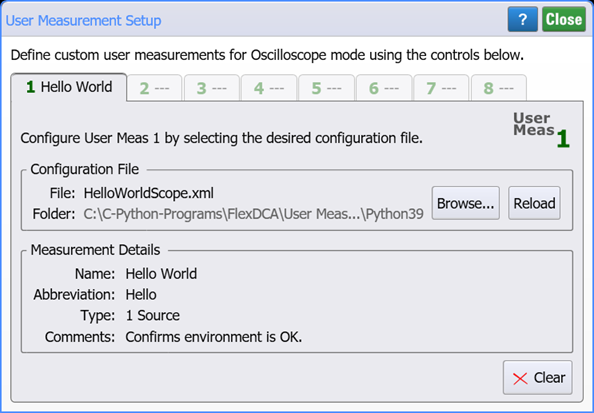
HelloWorldScope.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Measurement>
<Name>Hello World</Name>
<Abbreviation>Hello</Abbreviation>
<Comments>Confirms environment is OK.</Comments>
<Script>HelloWorldScope.py</Script>
<MeasurementType>1 Source</MeasurementType>
<ValidMode>Scope</ValidMode>
</Measurement>
HelloWorldScope.py
# Python 3 FlexDCA User Measurement
def algorithm(variables):
SrcData = variables['SrcData']
num_samples = len(SrcData)
if num_samples == 0:
return {'ErrorMsg': 'No data'}
print('Hello World!')
return {'Result': 4.2,
'Units':'dB',
'Status':'Correct',
'ErrorMsg':''}
Do not use spaces or hyphens when selecting a file name for your script.