How to start the Swept IMD Setup dialog
Using Hardkey/SoftTab/Softkey
Using a mouse
-
Press Freq > Main > IMD Setup....
-
Click Stimulus
- Select IMD Setup...
Other IMD (Opt S9x087A/B) Topics
Fast and easy setup for the measurement of a variety of distortion related parameters up to 9th order.
Measurement at both input and output of a DUT.
Supports a variety of sweep-modes for the main-tones: center-frequency linear and segment sweep, tone-separation sweep, power sweep, or CW sweep (fixed main-tone).
Make very fast, accurate measurements using the VNA sources with high-power, high linearity, and low harmonics.
Supports calibration and correction of Swept IMD parameters.
Independently set IFBW for measuring main-tones versus product tones.
2-port non-frequency converters ONLY. For frequency converters, use Swept IMDx.
DUT to VNA port mapping is limited. Port selections are made on the Power tab. Learn more.
When using Integrated Pulse application, the IF Filter setting for the relevant receiver must be changed to 'Wide'. Learn how. The default IF Filter setting in Swept IMD is 'Narrow' in order to avoid spurs and harmonics. The IF Attenuator setting (on the same dialog) may also require adjusting.
The following features are NOT available with Swept IMD:
Analog Sweep (Stepped sweep mode only)
Log frequency sweeps
Unratioed receiver measurements (A, B, R)
Save Formatted Citifile data.
Some Fixturing Features
External Test Set Control (Option S9x551A/B)
Integrated Narrowband or Narowband Pulse App
External DC Sources (DC Meters ARE supported).
Press Meas > S-Param > Meas Class....
Select Swept IMD, then either:
OK delete the existing measurement, or
New Channel to create the measurement in a new channel.
A Swept IMD measurement is displayed. To select additional parameters to display, click Response, then Meas, then select a parameter from the list.
How to start the Swept IMD Setup dialog |
|
|
Using Hardkey/SoftTab/Softkey |
Using a mouse |
|
|
|
Configures the Sweep Type and frequency range for SweptIMD and Swept IMDX measurements. Sweep Type and Sweep Settings
Segment Sweep Notes: (Swept IMD ONLY)
Number of Points Enter the number of data points for each sweep. See Limited Number of Acquisitions. IFBWThe Narrowband IF path is used for IMD measurements to help reduce spurious responses. Because the narrowband filter has a bandwidth of about 28 kHz, using an IFBW greater than 30 kHz does nothing to improve measurement accuracy. Main Tone and IM Tone IFBW IF Bandwidth is specified separately for the main tones (f1 and f2) and for the intermodulation tones. This allows the higher-power main tones to be accurately measured at a higher - and faster - IFBW, while the lower-power product tones to be accurately measured a lower - and slower - IFBW. Note: The IFBW is limited to 600 kHz when performing Swept IMD measurements even if the Wide IF path is selected. Reduce IF BW at Low Frequencies - On the VNA, the trace noise becomes worse below 748 MHz. This is especially obvious between 10 MHz and 45 MHz. When this box is checked, the VNA uses a smaller IF Bandwidth than the selected value at frequencies below 748 MHz. Learn more about the selected values. Note: For Main Tone IFBW settings of 1 kHz and below, and when the center frequency of the VNA is an exact multiple of 10 MHz, then the tone frequencies are shifted UP by (10* IFBW) for the entire IFBW sweep. If those frequencies would exceed the maximum frequency of the analyzer, then the frequency is shifted DOWN by (10 *IFBW). This is done to avoid interference with 10 MHz reference signals. |
|
Configures RF power and Power Sweep settings for IMD measurements. Power ON (All channels) Check to turn RF Power ON or clear to turn power OFF for all channels. DUT Input PortInput Port Choose Port 1 or Port 3. When using Port 3, an external combiner is required. Learn more. Source Attenuator Specifies the port 1 attenuator. This attenuator affects the range of available power into the DUT Learn more about Source Attenuation. Receiver Attenuator This attenuation setting protects the A receiver from damage. DUT Output PortOutput Port Choose Port 2 or Port 4 (with limitations), Learn more. Source Attenuator This setting is used to improve the load match at the DUT output. Select 0 dB for power levels up to 10 dBm, and increase by 10 dB for every 10 dBm more output power. Receiver Attenuator Specifies the attenuator setting for port 2. When the power into the receiver test port is around +10 dBm, the VNA receiver may be in compression. However, with receiver attenuation, lower input power levels may become too noisy to make accurate power measurements. In this case, lower IFBW for the IM tones to reduce noise. Learn more about Receiver Attenuation. Tone PowersCoupled Tone Power Check to set the same power level for each main tone using the f1 Power setting. Clear to set different f1 and f2 power levels. ALC On Check to use internal ALC hardware (default). Clear to use Open Loop hardware. Open Loop leveling should only be used when doing Wideband Pulse measurements. Power LevelingBecause the gain of the DUT can be different for the f1 and f2 tone frequencies, you can set tone power at either the input of the DUT OR the output using the following methods. Receiver Leveling will cause slower sweeps. Set Input Power (Default) The specified f1 and f2 power levels are set at the DUT input. Input power level accuracy is based ONLY on the source power cal that is performed during the IMD cal. The input and output tones may NOT be equal or flat. Set Input Power, receiver leveling The specified f1 and f2 power levels are set at the DUT input using receiver leveling at the input reference receiver. This ensures the tone power levels are equal at the DUT input. However, the output tones may NOT be flat due to variations in the gain of the DUT at different frequencies. Set Input Power, equal tones at output The specified f1 and f2 power levels are set at the DUT input and a measurement is made at the output. The inputs are adjusted once at each frequency to ensure the tone power levels are equal at the DUT output. However, the output tones may NOT be flat due to variations in the gain of the DUT at different frequencies. Set Output Power, receiver leveling The specified f1 and f2 power levels are set at the DUT output. Receiver Leveling at the output receiver is used to accurately set the specified power level of each tone within the tolerance value that is set in the Receiver Leveling dialog. This setting results in the output tones being equal and flat across the frequency range. Note: Enabling Safe Mode when using receiver leveling may be necessary to ensure stable results. f1 / f2 PowerFixed f1 Power Specify the power level for f1 at either the DUT input or output depending on the Power Leveling setting. Choose a value between -30 dBm and +30 dBm. When "Coupled Tone Power" is checked, power is set for both f1 and f2 tones. Fixed f2 Power Available when Coupled Tone Power is NOT checked. Specify the power level for f2 at either the DUT input or output depending on the Power Leveling setting. Choose a value between -30 dBm and +30 dBm. Start, Stop, and Step f1 and f2 Power Available when Power Sweep is selected on the Frequency tab. Sets the Start and Stop power levels for f1 and f2, either individually or together with Coupled Tone Power checked. Path Configuration click to launch the RF Path Configuration dialog. Highlighted Note: RF2 tone power offset to compensate for combiner loss. This message appears when the f2 tone is being supplied by an external source. The tone power has been increased on the external source to compensate for loss through the internal combiner. For example, if the tone power at the DUT should be 0 dBm, the power out of the source will be about 15 dB higher. |
|
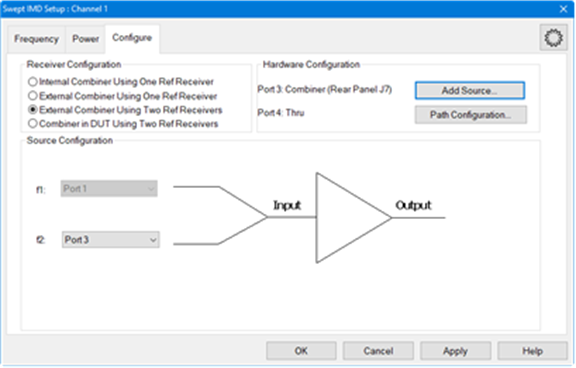
Receiver ConfigurationNote: Multiple Receiver Configurations is a Licensed Feature. Learn more about Licensed Features. Internal Combiner Using One Ref Receiver - This configuration is supported on the PNA-X only and is the default mode. This configuration is one reference receiver + internal combiner mode. External Combiner Using One Ref Receiver - This configuration is one reference receiver without internal combiner on the PNA-X. External Combiner Using Two Ref Receivers - This configuration uses two reference receivers for two input tones. Each port uses its own reference receiver. Combiner in DUT Using Two Ref Receivers - This configuration uses two reference receivers for two input tones applied to a combiner inside the DUT. Each port uses its own reference receiver. Source ConfigurationTo accommodate single-source VNA models, an external source can be used for the f2 tone. Learn how to configure an external source and combiner to make Swept IMD and IMDx measurements. f1 Always uses VNA internal source 1. f2 Select a source to be used for the f2 tone. This selection is available when an external source is configured and the Active box is checked on the External Source Configuration dialog. Hardware ConfigurationAdd Source Click to configure an external source using the External Source Configuration dialog. Path Configuration Click to launch the Path Configuration dialog (PNA-X models only). |
|
Use this dialog to select IMD and IMDx parameters to measure and display. Up to five parameters can be selected at a time, then click Apply to create those traces. Then select more without closing the dialog. There is no limit to the number of traces and windows allowed in the VNA. Note: Calculations are NOT performed to determine if the frequency of a selected intermod (Order) product will be within the frequency range of the VNA. Measurements that fall outside of the frequency range of the VNA are displayed as -200 dB. Param Name This name is built from the selected Type, Tone Select, Order, and Measure At settings. Once built, check to measure this parameter. TypeSelect the type of Swept IMD measurement to make. The characters below (in parenthesis) are used in the Param Name.
Tone SelectSelect the tone (High, Low, or Both) to be measured and displayed (See image).
Used to build the parameter name:
OrderSpecify the intermodulation product to measure. Choose from 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9.
Measure AtMeasure the selected parameter at either: DUT Input
DUT Output
|
At the first page of the IMD Cal Wizard, you tell the calibration routine the frequencies at which the calibration is to be performed. Optionally, you can choose to perform the source power cal at only the center frequency midway between the main tones. For IMDx ONLY, you can also choose to perform a source power cal of the LO source.
The VNA calculates an array of source and receiver frequencies that incorporate all the main tone frequencies (low and high) and the specified product tone frequencies.
Using a power meter at port 1, a source and receiver calibration is performed to calibrate the R1 reference receiver to be a fast and 'tunable' power meter.
The R1 reference receiver is then used to perform a source power cal of the main tone frequencies: first the Source 1 / Low tone then the Source 2 / High tone. Both sources are left ON while each tone is measured in order to duplicate the impedance match under which the measurement will be performed.
Then a standard 2-port SOLT cal is performed at all frequencies using either an ECal module or mechanical standards. The 2-port cal is used to correct the source calibration R1 tracking terms for the match of the power sensor. It is also used to transfer the R1 tracking term to the B receiver.
If the main tone frequencies change but are within the frequency range in which the calibration was performed, then the calibration becomes interpolated C*. This can occur by changing the start/stop/center/span frequencies, the number of points, or the sweep type. Learn more about Interpolation.
A Preference setting can be made which allows a Swept IMD and IMDx calibration to exceed the stop frequency limit of an ECal module. Learn more.
Receiver calibrations that are performed in a standard channel can be applied to a Swept IMD channel. However, Source Calibrations can NOT be applied.
The Cal All wizard supports calibration of the two reverence receiver configurations (external combiner and combiner in DUT).
In the Configure tab, select External Combiner Using Two Ref Receivers:
Press Cal > Other Cals > Cal All.... The Calibrate All Selected Channels dialog is displayed:
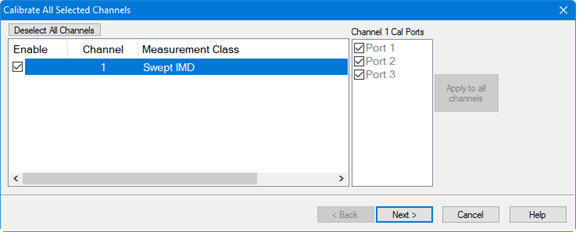
Receiver Calibration: Connect the power sensor to the Cal Plane (Cal Plane is the output of the external combiner). The R1 and R3 receivers will be calibrated with the power sensor.
Source Calibration: After the R1 and R3 receivers are corrected, both Port 1 and Port 3 are turned on, then Port 1’s source is calibrated with corrected R1 and Port 3’s source is calibrated with corrected R3.
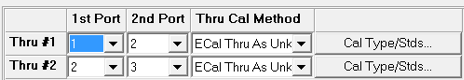
S-Parameter Calibration: Because Port 1 and Port 3 share one Cal Plane, Thru 1-3 is removed by the software and only keeps two Thrus:
The following shows an actual measurement with leveling turned on.
How to start a Swept IMD Calibration |
|
|
Using Hardkey/SoftTab/Softkey |
Using a mouse |
|
|
|
Calibration ModeMatch corrected Response Cal This selection performs a full IMD calibration as described in the above Calibration 'Overview'. Response ONLY (Normalization) This IMD Cal does NOT correct for the mismatch of the power sensor. Choose this if you have a test configuration that does not easily accommodate making match measurements. Instead of a standard 2 port SOLT cal (Step 5 above), only the transmission tracking term is measured and used to transfer the R1 receiver tracking term (produced by the power sweep) to the B receiver. Note: For the Response (Normalization) Cal, it is assumed that a zero-length THRU standard is being used to connect port 1 to port 2. If an adapter is used, there is NO compensation for delay or loss of the adapter. This can NOT be changed. Tone Power CalCalibrate only at center frequencies The source power cal portion is performed at only the center frequency, which is midway between the main tones. This cuts the source power calibration time (the slowest part of the calibration) in half. The measurement is interpolated although the C* annotation is not shown in the status bar. Calibrate at all frequencies The source power cal portion is performed at all main tone frequencies. Enable LO Power Calibration (IMDx ONLY) Check to perform a standard power calibration of the LO source as part of the calibration process. Select Product TonesMax Product Select the highest product that you will be measuring. The low and high frequencies for that product, and all lower 'odd' order products will be calibrated. For example, when 5th Order Product is selected, the frequencies for the Main Tones, and the Low and High order products for the 3rd and 5th order products will be included in the calibration. Include 2nd Order Products Check to calibrate the 2nd-order products in the frequencies to be calibrated. The frequencies of these products are usually far from the main tones. Extrapolated ECal CalibrationA Preference setting can be made which allows a Swept IMD and IMDx calibration to exceed the stop frequency limit of an ECal module. The error terms beyond the ECal stop frequency are extrapolated. The setting is designed to provide correction for order products (especially 2nd order) when the frequencies exceed the ECal module stop frequency.
|
|
Select DUT Connectors and Cal Kits - IMD Cal dialog box help |
|
If Response Only is selected on the previous page, click Source Cal Settings... to change the Source Cal settings, or click Next> to continue. Otherwise, this is a standard VNA Cal Wizard page except for the following: Modify Cal Check, then click Next, to Modify Cal (Standards AND Thru Method). Source Cal Settings Click to launch the Source Cal Settings (for Apps) dialog. |
|
Power Cal Settings - IMD Cal dialog box help |
|
A power calibration is performed on port 1. This is done to simplify subsequent IMD calibrations since the power calibration will not need to be repeated. For highest accuracy, connect the power sensor directly to the test port with no adapter. |
|
Power Level at which to perform the Port 1 Source Power Cal. It is usually best to perform the Source Power Cal at 0 dBm because the power sensor is calibrated at that level. However, if a component is used between the VNA source and the calibration reference plane, then adjust the power level so that the power at the sensor is about 0 dBm if possible. |
The remaining dialog pages are the same as the standard Cal Wizard.
Swept IMD power data, Log Mag ONLY, can be saved to a *.csv file. This data type can be read by spreadsheet programs, such as Microsoft Excel. Data from the last complete sweep is saved to the specified *.csv file.
How to save Swept IMD (and IMDx) dataWith a Swept IMD or IMDx channel active... |
|
|
Using Hardkey/SoftTab/Softkey |
Using a mouse |
|
|
Notes:
For every tone, six power levels are saved in this order: OUT Avg | OUT Lo | OUT Hi | IN Avg | IN Lo | IN Hi
Power levels for the Main tones are always saved, regardless of the active measurement.
All tones that are displayed are also saved. For example, any displayed 3rd order tone parameter causes the 3rd tone power levels to be saved.
Only tone powers are saved. Calculated parameters, such as IMD Relative to Carrier (IM) are NOT saved.
If calibration is turned ON when the file is saved, then all data is calibrated. Otherwise, raw data is saved.
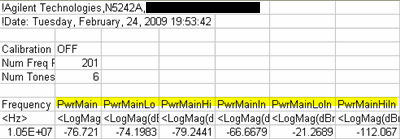
This image shows the 6 Main tone power levels that are always saved.
In the power parameter labels, Output and Avg are implied as in the parameter selection. For example: PwrMain = Average Output power of the main tones.