Call Processing Status
Last updated: January 15, 2009
- Call Processing Status
-
Active Cell Connection State
- Call Connection State
- Data Connection State ( lab application only )
Call Processing Status
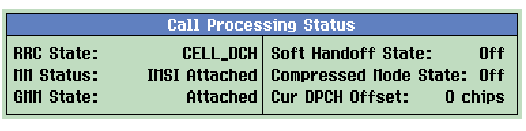
The
Call Processing Status
window on the
Call Setup
screen displays the following information when in
Active Cell Operating Mode
:
-
RRC State
This functionality is present in the lab application only.
RRC Stateindicates whether the RB Test Mode service has set the UE up into aCELL_FACHorCELL_DCHstate, or isIdle. See RB Test Mode RRC State Setting and Radio Bearer Test Mode Origination to CELL_FACH .GPIB command: CALL:STATus:RRC:STATe? .
-
MM Status
MM Statusindicates whether the UE has registered, and what type of registration (Location Updating procedure) was last performed (see Performing a Location Update (CS Domain Registration) ). When the UE registers with the network, its Location Updating Request message includes a Location Updating Type information element that can have a value of "Normal location updating", "Periodic updating" or "IMSI attach" (see 3GPP TS 24.008 s4.4.1, s9.2.15 and s10.5.3.5).-
Updated (normal): Indicates that the last Location Updating procedure was of the type "Normal location updating". Normal location updating is used to update the network with the actual Location Area of a UE (for example when the UE enters a new location area). -
Updated (periodic): Indicates that the last Location Updating procedure was of the type "Periodic updating" (the UE performed a timer-based registration). Periodic updating is used to notify periodically the availability of the UE to the network. The procedure is controlled by the T3212 Periodic Location Update Timer . -
IMSI Attached: Indicates that the last Location Updating procedure was of the type "IMSI attach" (the UE performed a power-up registration). The IMSI attach procedure is used to indicate the IMSI as active in the network. -
IMSI Detached: Indicates that the UE sent an IMSI Detach Indication message to the test set (the UE performed a power-down registration). This occurs when the UE was IMSI Attached and then was powered down or its USIM was removed. -
None: The UE has not registered with the test set (MM Statusis also set toNonewhen you clear the UE information (see Clear UE Info ).
GPIB command: CALL:STATus:MM? .
-
-
GMM State
GMM Stateindicates the result of the most recent GPRS attach or detach. It is set toAttachedwhen the UE has successfully completed the GPRS Attach procedure andDetachedon completion of the GPRS Detach procedure. If the UE sends the test set an Attach Request but never responds to the Attach Accept with an Attach Complete, then it is set toAttach Incomplete. GMM state is cleared when you clear the UE information (see Clear UE Info ) and is set toNoneon power up and preset.See Packet Switched Data .
GPIB command: CALL:STATus[:GMM]:ATTached:STATe? .
-
Soft Handover State
This functionality is present in the lab application only. See Soft Handover .
GPIB command: CALL:STATus:SHANdoff:STATe? .
-
Compressed Mode State
This functionality is present in the lab application only. See Compressed Mode .
GPIB command: CALL:STATus:COMPressed:STATe? .
-
Current DPCH Offset
Current DPCH Offsetreports the DPCH Frame Offset (tau DPCH ) currently in use by the test set (for the current operating mode).DPCH Frame Offset is the offset of the DL DPCH to the P-CCPCH (see 3GPP TS 25.331 s10.3.6.21 and 25.211 Figure 29). 3GPP prescribes several rules around changing DPCH Frame Offset, which can be changed using the Default DPCH Offset IE (which has a resolution of 512 chips) or the DPCH Frame Offset IE (which has a resolution of 256 chips).
Per 3GPP, during a timing re-initialized reconfiguration (Timing Indication IE = Initialise), the Default DPCH Offset IE and DPCH Frame Offset IE in the reconfiguration message must be set to the same value. This means the resolution of the timing adjustment on a timing re-initialized reconfiguration is 512 chips. See 3GPP TS 25.331 s8.3.5.1.2.
Per 3GPP, during a timing maintained reconfiguration (Timing Indication IE = Maintain), the reconfiguration message must not include a Default DPCH Offset IE; only the DPCH Frame Offset IE is signalled. However, if the UE is ordered to adjust its timing by more than 256 chips, then it will reject the reconfiguration. This means the resolution of the timing adjustment on a timing maintained reconfiguration is 256 chips, but the maximum timing change is 256 chips. See 3GPP TS 25.331 s8.2.2.3.
Per 3GPP, there is a further constraint on when DPCH Frame Offset can be changed. According to 3GPP 25.331 v5.17.0 s8.6.6.28, timing re-initialized reconfigurations are intended to be exclusively used for hard handovers (i.e. where the UE changes UARFCNs and/or all Primary Scrambling Codes for all links in the active set as part of the reconfiguration, see 3GPP TS 25.331 v5.17.0 s8.6.6.3a). 25.331 states that the UE's behavior is undefined if the network sets the Timing Indication IE to Initialise on a non-hard handover (i.e. where the UARFCNs and one or more Primary Scrambling Codes remain unchanged as part of the reconfiguration). Therefore, to change DPCH Frame Offset using the Default DPCH Offset IE (i.e. to a value of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 x 512 chips), you must also change UARFCNs or Primary Scrambling Codes during the reconfiguration.
In active cell operating mode, the test set can signal the DPCH Frame Offset to the UE in one of two ways:
-
During call establishment, using the
Default DPCH Offset (DOFF)
setting: Sets DPCH Frame Offset to 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 x 512 chips during call establishment (you cannot change the
Default DPCH Offset (DOFF)setting while on a connection, you must set it before establishing the connection). -
While on a connection, using the following settings:
-
RBRor TCR Default DPCH Offset (DOFF) : Sets DPCH Frame Offset to 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 x 512 chips while on a connection (using a Radio Bearer Reconfiguration or Transport Channel Reconfiguration, respectively). Note, 3GPP TS 25.331 v5.17.0 s8.6.6.28 states that the timing re-initialized reconfiguration required to send the Default DPCH Offset IE must also include a change in UARFCN or Primary Scrambling Code, or the UE's behavior is undefined. Both the Radio Bearer Reconfiguration and Transport Channel Reconfiguration can be used to change UARFCNs. -
RBRor TCR Relative DPCH Frame Offset : Changes the current DPCH Frame Offset by -256, 0 or +256 chips while on a connection (using a Radio Bearer Reconfiguration or Transport Channel Reconfiguration, respectively).
-
In FDD test operating mode, you can set DPCH Frame Offset to 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, or 10 x 256 chips using the DPCH Frame Offset setting. Note, you must then also set this DPCH Frame Offset in the UE so that it can successfully decode the test set's signal; the test set does not provide any signalling to the UE in FDD Test Operating Mode and thus will not signal the DPCH Frame Offset setting to the UE.
Current DPCH Offsetis not displayed on the front panel screen while in FDD test operating mode because in FDD test operating mode,Current DPCH Offsetis always equal to theDPCH Frame Offsetsetting.In active cell operating mode, if a DL DPCH is not active,
Current DPCH Offsetsimply reflects the value of theDefault DPCH Offset (DOFF)setting.GPIB command: CALL:STATus:DPCHannel:OFFSet?
Implications of the Current DPCH Offset
The UL DPCH is always transmitted 1024 chips after the DL DPCH. Thus, changing DPCH Frame Offset, which offsets the DL DPCH from the P-CCPCH, changes the offset between the UL DPCH and P-CCPCH by the same amount.
When on an HSDPA or HSPA connection (lab application or feature licensed test application only) , changing the DPCH Frame Offset results in a change in the offset between the UL DPCH and HS-DPCCH, because the HS-DPCCH is always transmitted 12.5 slots after the start of the HS-SCCH (which is always aligned to the P-CCPCH). In other words, changing the DPCH Frame Offset shifts the UL DPCH's position in time relative to the HS-DPCCH.
The following table indicates the time offset present between the HS-DPCCH and UL DPCH for the various DPCH Frame Offset values available in the test set.
-
During call establishment, using the
Default DPCH Offset (DOFF)
setting: Sets DPCH Frame Offset to 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 x 512 chips during call establishment (you cannot change the
Active Cell Connection State
Additional call processing state information is also displayed in the small
Active Cell
window at the bottom of the
Call Setup
screen. Note that for single services, the respective
Call Connection State
or
Data Connection State
is displayed. When
Simultaneous Services
is active the
Active Cell
window displays both the call connection state and the data connection state (in that order) separated by a "/".

Call Connection State
The call connection state can transition between the following states:
-
Alerting (CALL)
Alerting is returned when the test set is alerting the UE to an incoming AMR voice call request.
-
Connected (CONN)
Connected is returned when the test set and UE are connected on a call.
-
Handoff (HAND)
Handoff is returned when the test set is in the process of handing off the UE.
- Idle (IDLE)
-
Paging (PAG)
Paging is returned when the test set is in the process of paging the UE.
-
Registering (REG)
Registering is returned when the test set is in the process of performing a registration with the UE.
-
Releasing (REL)
Releasing is returned when the test set is in the process of releasing the UE from a call using over the air signalling as part of a UE or test set originated release procedure.
-
Setup Request (SREQ)
Setup Request is returned when the test set is in the process of assigning a channel to the UE as part of a page or a UE-originated call setup.
GPIB commands: CALL:STATus[:STATe][:VOICe]? and CALL:CONNected[:STATe]
Data Connection State
The data connection state can transition between the following states:
- Idle (IDLE)
- Attaching (ATTG)
- Detaching (DET)
- Off (OFF) - state when the test set powers up or is preset
- PDP Activating (PDPAG)
- PDP Active (PDP)
- PDP Deactivating (PDPD)
GPIB command: CALL:STATus[:STATe]:DATA?