FDD Test Operating Mode
- FDD Test Overview
- Synchronizing the UE to the Test Set's Downlink to Make Measurements
- Additional FDD Test Mode Settings
- FDD Test Operating Considerations
- HSDPA in FDD Test Operating Mode (lab application or feature-licensed test application only)
- HSPA in FDD Test Operating Mode (lab application or feature-licensed test application only)
FDD Test Overview
In
FDD Test (frequency division duplex)
Operating Mode , the test set does not send any signalling
information on the downlink. Any changes to the UE configuration,
such as channel, loopback type, or dedicated physical channel
(DPCH) scrambling code, must be accomplished by directly sending
commands to the UE from a system controller (usually a personal
computer) through a proprietary digital interface.
Upon entry into test mode, the test set begins continuously transmitting a downlink signal which consists of a dedicated physical channel (DPCH) configured as the specified symmetrical reference measurement channel (see Symmetrical RMCs ) and several overhead channels required to allow the UE to synchronize to the test set and decode transmitted data (see Downlink and Uplink Channels Overview ). When HSDPA is active ( for lab applications and feature-licensed test applications only ), the test set also transmits up to 5 HS-PDSCHs (as determined by the FDD Test "FRC Type" setting) and up to 4 HS-SCCHs (see HSDPA in FDD Test Operating Mode ).
The UE must synchronize to the transmitted downlink channels and transmit the proper corresponding uplink signal(s). The UE's performance can then be measured using the suite of measurements available in the test set. To emulate interference from other cells or users, two noise sources (OCNS and AWGN) can be added as desired.
The following
example selects FDD Test operating
mode via GPIB:
OUTPUT 714;"CALL:OPERating:MODE FDDT"
Synchronizing the UE to the Test Set's Downlink to Make Measurements
The following test set controls must match your UE configuration to allow it to synchronize to the test set's downlink signal and transmit an uplink signal that the test set can receive and measure:
Cell Power - The power level out of the test set must be high enough for the UE to receive the downlink signal and decode the data.
-
Channel Type - The UE must support Symmetrical RMCs . The UE must be configured to transmit the RMC to which
Channel Typeis set. -
Uplink DPCH Scrambling Code - You must set this to the scrambling code the UE is using to transmit its uplink signal. This setting tells the test set which scrambling code to use to decode the uplink signal from the UE.
-
RF Gen Freq CtrlThe
RF Gen Freq Ctrlsetting is only applicable to theFDD Testoperating mode. When changing between operating modes, theRF Gen Freq Ctrlsetting is returned to its default value ofAuto.GPIB command: CALL[:CELL]:CONTrol:DOWNlink:FREQuency:AUTO .
Manual operation: F11 on the
Call Parms 3 of 3menu.The UE must be set to receive the downlink signal on the proper frequency. You can set the downlink frequency manually or automatically, depending upon the
RF Gen Freq Ctrlsetting.- When
RF Gen Freq Ctrlis set toAuto, the downlink frequency is determined by the DL Channel setting. -
RF Gen FreqWhen
RF Gen Freq Ctrlis set toManual, the downlink frequency is determined by theRF Gen Freqsetting. TheRF Gen Freqsetting is only applicable toFDD Testoperating mode and CW Operating Mode (inCWoperating mode, generator frequency control is always manual).GPIB command: CALL[:CELL]:RFGenerator:FREQuency .
Manual operation: F7 under
Channel (UARFCN) Parms( F12 on theCall Parms 1 of 3menu).
- When
-
Uplink Frequency / Uplink Channel - You must indicate at what frequency the UE is transmitting. You can specify the uplink frequency or uplink channel.
-
Measurement Frequency - You must indicate at what frequency the test set should perform measurements. You can specify this frequency manually, or automatically set the measurement frequency to match the Uplink Channel setting.
-
Downlink Channel Codes - The UE must be set to expect the following code settings from the test set on the downlink:
Shared DL Channel Codes: Primary Scrambling Code - This value must match the downlink scrambling code the UE expects in order for the UE to decode the downlink channels and synchronize to the test set.-
Shared DL Channel Codes: PICH Channelization Code - You can not perform the Paging procedure while in FDD test operating mode, but you may choose to send DL PICH Data on the PICH. If so, you must specify the PICH channelization code the UE expects. -
WCDMA DL Channel Codes: DPCH channelization code - This value must match the DPCH channelization code the UE expects.
- DPCH
Frame Offset
You can set the DPCH Frame Offset to 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, or 10 x 256 chips (see Current DPCH Offset for more information about DPCH Frame Offset). Note, you must then also set this DPCH Frame Offset in the UE so that it can successfully decode the test set's signal; the test set does not provide any signalling to the UE in FDD test operating mode and thus will not signal the DPCH Frame Offset setting to the UE.
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:DPCHannel:FOFFset
-
Power Control / Manual Power / UE Target Power - You must indicate the power level at which the UE is expected to transmit, so the test set can properly range its receivers.
-
UE Loopback Type - When performing receiver tests, you must set
UE Loopback Typeto the loopback type the UE is set to use (the test set does not signal the loopback type to the UE). -
UL CL Power Ctrl ParametersSee Uplink Closed Loop Power Control Parameters and UE Target Power .
-
FDD Test UL CL Power Ctrl ModeIf you set
FDD Test UL CL Power Ctrl ModetoActive bits, be sure to set FDD Test UL CL Power Ctrl Algorithm and FDD Test UL CL Power Ctrl Stepsize to the values being used by the UE, so that the test set can successfully drive the UE's power to the UE Target Power setting. The test set does not signal the power control algorithm or step size to the UE. Also, if Uplink DPCH Bc/Bd Control is set toManual, ensure that Manual Uplink DPCH Bc and Manual Uplink DPCH Bd are set to match your UE's operation.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:CLPControl:UPLink:MODE .
-
FDD Test UL CL Power Ctrl AlgorithmGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:CLPControl:UPLink:ALGorithm .
-
FDD Test UL CL Power Ctrl StepsizeGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:CLPControl:UPLink:STEPsize .
- Send Step Up/Down TPC Bit Pattern
-
-
Uplink Parameters- Ensure that Bc and Bd are set to match your UE's configuration. - DL
TFCI Pattern
This setting is only applicable to
FDD Test Operating Mode.You must indicate what value the test set should transmit in the TFCI field (see 3GPP TS 25.331 10.3.5.16). You can set
DL TFCI Patternto any value between000and3FF(0 to 1023). You must setDL TFCI Patternto the value that corresponds to the RMC Transport Format Combination in the Transport Combination Set (TFCS) you've provided to the UE.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:TFCIndicator .
- Uplink
TFCI Control
This setting is only applicable to
FDD Test Operating Mode.When
Uplink TFCI Controlis set toAuto, the test set uses the TFCI value sent by the UE on the DPCCH. The test set uses the standard RMC TFCI table to interpret the received TFCI: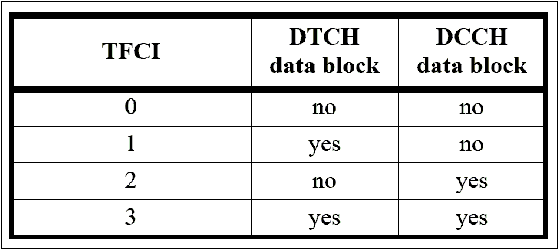
When Uplink TFCI Control is set to
Manual, the test set ignores the TFCI value sent by the UE and uses the value specified by the Manual Uplink TFCI setting.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:UPLink:TFCIndicator:CONTrol:AUTO
Manual operation:
Uplink Parameters(F4) on theCall Control 2 of 2menu. - Manual
Uplink TFCI
This setting is only applicable to
FDD Test Operating Mode.When Uplink TFCI Control is set to
Manual, this setting determines whether the test set expects just the DTCH (DTCH Only) or the DTCH plus DCCH (DTCH + DCCH) on the uplink DPCH.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:UPLink:TFCIndicator:MANual
Manual operation:
Uplink Parameters(F4) on theCall Control 2 of 2menu.
Additional FDD Test Mode Settings
-
DL PICH DataThis setting is only applicable to
FDD Test Operating Mode.The paging indicator channel can be set to transmit either all zeroes or all ones.
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:PICHannel:DATA .
-
WCDMA DL Channel LevelsFDD Test CPICH LevelGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:CPIChannel[:SLEVel] .
-
FDD Test P-CCPCH/SCH LevelGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:CCPChannel:PRIMary[:SLEVel] .
-
FDD Test PICH LevelGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:PICHannel[:SLEVel] .
-
FDD Test DPCH LevelGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:DPCHannel[:SLEVel] .
-
FDD Test Antenna 2 P-CPICH LevelGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel[:SLEVel]:HSDPa CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel[:SLEVel]:HSPA .
-
FDD Test Antenna 2 S-CPICH LevelGPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel:SECondary[:SLEVel]:HSDPa CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel:SECondary[:SLEVel]:HSPA .
-
Compressed Mode (lab application only) - see Compressed Mode Operation While in FDD Test Operating Mode .
FDD Test Operating Considerations
The test set can perform loopback bit error ratio (BER) measurements if the UE provides a loopback mode that conforms to 3GPP TS 34.109, section 5.3.2.6.2, Loopback of RLC SDUs . Additionally, the uplink DPDCH transport format must be set so both the dedicated traffic channel (DTCH) and dedicated control channel (DCCH) are present (however, the test set will ignore the contents of the DCCH so the actual content of this channel is not relevant).
When the test set and the UE are synchronized, the UE uplink frame starts 1024 chips after the receiving the corresponding downlink frame. Measurements that require synchronization will not trigger correctly (or at all) if this timing relationship does not exist.
In FDD Test operating mode, the test set does not negotiate with the UE to set up a call, or provide any other form of interactive control of the UE (other than uplink closed loop power control, see UL CL Power Ctrl Parameters ). You can select the transport format indication (TFCI) pattern sent to the UE on the downlink, but the test set does not assume or verify that the UE responded. The test set ignores transport format combination indicator (TFCI) and transmit power control (TPC) bits sent on the uplink.
HSDPA in FDD Test Operating Mode
This section is only applicable to the lab application or feature-licensed test application.
HSDPA Activation in FDD Test
In
FDD Test operating mode, HSDPA is active when
Channel Type is set to 12.2k
RMC + HSDPA .
HSDPA Operation in FDD Test
When HSDPA is active, in addition to the 12.2k RMC and common channels, the test set transmits up to 5 HS-PDSCHs (as determined by the FDD Test "FRC Type" or FDDT "User Defined Number of Active HS-PDSCHs" settings) and up to 4 HS-SCCHs. The test set also generates a six-channel OCNS as specified by 3GPP TS 34.121 sE.5.2 (codes 122 - 127, spreading factor 128), rather than the OCNS defined in sE.3.6 (see OCNS in HSDPA/HSPA ).
When HSDPA is active, the test set expects the UE to transmit a 12.2k RMC as well as an HS-DPCCH that contains ACK/NACK information corresponding to the downlink HS-PDSCH data. The HSDPA Information window displays counters to help you monitor the HSDPA connection status. Note, the test set expects an uplink DPCCH to be present when an uplink HS-DPCCH is transmitted (otherwise the HS-DPCCH can not be decoded as there are no pilot bits in the HS-DPCCH).
In
FDD Test operating mode, the test set does not signal the Ack-Nack Repetition Factor to the
UE, you must set the value manually in the UE. To ensure valid
HSDPA BLER results, you must ensure that the minimum inter-TTI
of the active HSDPA channel is greater than or equal to 2 ms * Ack-Nack Repetition Factor (so
that there is sufficient space on the uplink for the ACK/NACK
repeats to be transmitted). See Ack-Nack Repetition
Factor for more information about this requirement.
In
FDD Test operating mode, the test set does not signal the CQI Feedback Cycle (k) or CQI Repetition Factor to the UE,
you must set the values manually in the UE. To ensure a valid
Median
CQI result, you must ensure that
CQI Feedback Cycle (k) is greater than or equal to CQI Repetition Factor * 2ms (so
that there are no collisions between new and repeated CQI information).
See CQI
Transmission Settings for more information about this requirement.
The following diagram illustrates the HSDPA FDD test mode configuration in the test set, as well as the expected channels from the UE:
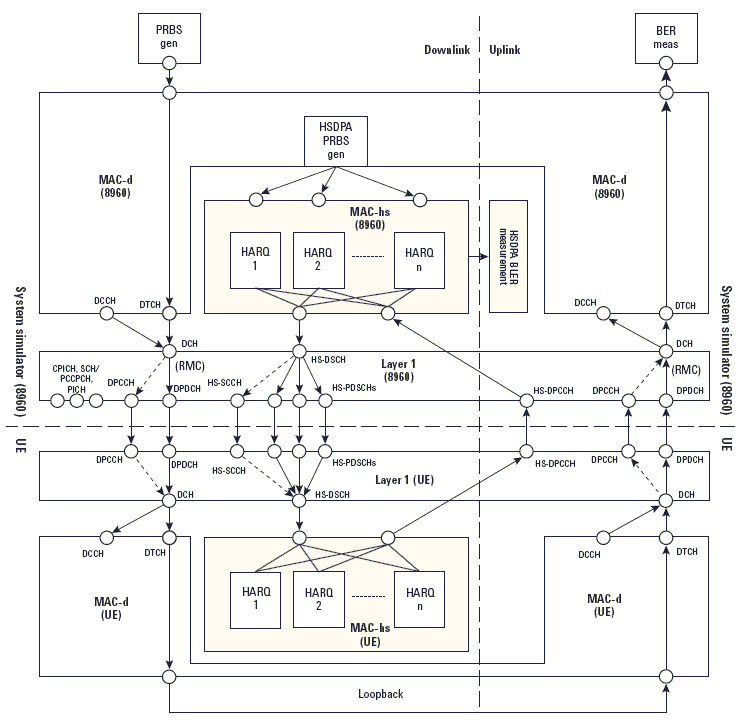
To test HSDPA UEs in FDD test mode, you must synchronize the UE and test set as described in Synchronizing the UE to the Test Set's Downlink to Make Measurements .
Additionally, you must consider the following:
Channel Typemust be set to12.2k RMC + HSDPA( CALL:SERVice:RBTest:RAB ).-
You must ensure that you have properly configured the
HSDPA Parameters( F10 on theHSPA Parametersmenu):HS-DSCH Parameters
- FDD Test
RB Test HS-DSCH Configuration Type
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:CONFig[:TYPE]
- FDD
Test FRC Type
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:FRC:TYPE .
- FDD
Test RB Test User Defined DC-HSDPA State
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:DCHSdpa[:STATe]
- FDD
Test HSDPA MIMO State
When the
FDD Test HS-DSCH Configuration Typeis set toUser Defined, and the FDD Test HS-DSCH MAC Entity isMAC-ehs, this setting controls whether to configure the MIMO or not in the serving cell when operating in the FDD Test Mode.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MIMO[:STATe]
- FDD
Test Mode Number of Transport Blocks
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:MIMO:TBLock:COUNt
- FDD
Test Primary Precoding Weight
When
Current MIMO Configuration Stateis set toActive, this setting specifies how the test set determines its downlink primary precoding weight in FDD Test Mode FRC configuration type.- If Primary Precoding Weight Config
is set to
Static, FDD Test Static Primary Precoding Weight is used as the primary precoding weight. - If
Primary Precoding Weight Config is set to
34.121-1 s9.2.4, the downlink primary precoding weight will be determined as per the specification in the 3GPP TS 34.121-1 section 9.2.4 (TTI basis).
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:FRC:MIMO:PPWeight:CONFig
- If Primary Precoding Weight Config
is set to
- FDD
Test Static Primary Precoding Weight
When
Current MIMO Configuration Stateis set toActiveand FDD Test Primary Precoding Weight is set toStatic, this setting specifies the downlink primary precoding weight in FDD Test Mode.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:MIMO:PPWeight[:STATic]
- FDD
Test N_cqi_typeA/M_cqi Ratio
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:MIMO:NMRatio
- FDD
Test User Defined HS-DSCH MAC Entity
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MAC
- FDD
Test User Defined 64QAM State
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:QAM64:STATe
- FDD
Test User Defined MAC-ehs HS-DSCH TB Size
Table
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MACEHS:TBSTable:ALIGnment
- FDDT
User Defined Number of Active HS-PDSCHs
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:HSPDschannel:COUNt
- FDDT
User Defined Transport Block Size Index
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:TBSize:INDex
- FDD
Test User Defined Modulation Type
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MODulation[:TYPE]
- FDD
Test Secondary TB Size Index
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:STBSize:INDex
- FDD
Test Secondary TB Modulation Type
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:STBLock:MODulation[:TYPE]
- FDD
Test User Defined Inter-TTI Interval
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:ITTI[:INTerval]
- FDD
Test User Defined Number of HARQ Processes
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:HARQ:PROCess:COUNt
- FDD
Test Number of HARQ Processes for MIMO
Sets the number of HARQ processes that are active in the MAC-ehs layer when FDD Test HSDPA MIMO State is set to
On.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MIMO:HARQ:PROCess:COUNt
-
FDD Test User Defined UE IR Buffer AllocationControls how the IR buffer size for each active HARQ process is determined.
When
FDD Test User Defined UE IR Buffer Allocationis set toImplicit, the total IR buffer size for the FDD Test UE HS-DSCH Category ("total number of soft channel bits" in 3GPP TS 25.306 Table 5.1a) is divided equally among the active HARQ processes. Note that to configure the user defined downlink to emulate an FRC, you may need to setUser Defined UE IR Buffer AllocationtoExplicit, and then set FDDT "User Defined Explicit UE IR Buffer Size" accordingly (see Example User Defined Configuration: Configuring the Downlink as an FRC ).When
FDD Test User Defined UE IR Buffer Allocationis set toExplicit, the IR buffer size allocated to each active HARQ process is determined directly by the FDDT "User Defined Explicit UE IR Buffer Size" setting. This setting allows you to allocate less than your UE's maximum total IR buffer size (which may be required if you wish to emulate an FRC, see Example User Defined Configuration: Configuring the Downlink as an FRC ).GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MS:IREDundancy:BUFFer:ALLocation
- FDDT
User Defined Explicit UE IR Buffer Size
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MS:IREDundancy:BUFFer:SIZE[:EXPLicit]
-
FDD Test UE HS-DSCH CategoryWhen FDD Test User Defined UE IR Buffer Allocation is set to
Implicit, this setting specifies the UE category to use for determining the IR buffer size.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:MS:CATegory
- FDD
Test HS-DSCH Data Pattern
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:DATA
-
FDD Test F-DPCH StateWhen the
Channel Typeis set toHSPA, this setting controls whether the F-DPCH is configured instead of the associated DPCH in the downlink while operating in FDD Test Mode.When FDD Test "RB Test User Defined DC-HSDPA State" is "ON", you can not set this parameter to "ON" because F-DPCH is not available with MAC-ehs.
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:FDPChannel:STATe
-
FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell 64QAM StateThis parameter controls whether the 64QAM encoding format defined in 3GPP TS 25.212 v8.6.0 s4.6 should be used for the secondary serving cell HS-SCCH. This setting is also used to determine the actual transport block size as described in the
Test Mode Def TB Size--Secondary Serving Cell.This setting is also involved in determining the HS-DSCH TB size table.
If FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell Modulation Type is "64QAM", you can not set this parameter to "Off".
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:QAM64:STATe
-
FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell HS-DSCH TBS TableThis setting selects the HS-DSCH TB size table when FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell 64QAM State is "Off". This setting is also used to determine the actual transport block size as described in Test Mode Def TB Size--Secondary Serving Cell.
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MACEHS:TBSTable:ALIGnment
-
FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell Active HS-PDSCHsThis setting controls how many HS-PDSCHs are active on the secondary serving cell.
You can not change this setting to a value that when added to the FDD Test First HS-PDSCH Channelization Code is greater than 16.
If you changes this setting to a new value results in a change the number of HS-PDSCHs such that there would be a collision in code-space, the test set will not block your operation and will still transmit using requested number of HS-PDSCHs, but the test set should detect collision and issue persistent error message. The persistent error message will be removed once the test set detected no collisions currently active channels.
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:HSPDschannel:COUNt
-
FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell TB Size IndexThis setting controls the transport block size index of the secondary serving cell and is used to determine the actual transport block size as described in
Test Mode Def TB Size--Secondary Serving Cell.GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:TBSize:INDex
-
FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell Modulation TypeThis setting controls the modulation type of the currently active HS-PDSCH channels on the secondary serving cell and is used to determine the actual transport block size as described in Test Mode Def TB Size--Secondary Serving Cell.
If FDD Test User Def Secondary Cell 64QAM State is "Off", setting this parameter to "64QAM" will be rejected.
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:MODulation[:TYPE]
-
FDD Test Def Sec Cell Inter-TTI IntervalThis setting controls the absolute inter-TTI interval between transmitting blocks to the UE on the secondary serving cell HS-PDSCHs.
GPIB Command: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSDSchannel:UDEFined:ITTI[:INTerval]
MAC-hs Parameters
FDD Test Number of Transmissions
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACHs:NTRans
-
FDD Test RV Sequence
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACHs:RVSequence
-
FDD Test RV Sequence for MIMO Primary Transport Block
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACEHS:PTBLock:RVSequence
-
FDD Test RV Sequence for MIMO Secondary Transport Block
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACEHS:STBLock:RVSequence
-
MAC-hs Transmit Window SizeThis setting is only used when MAC-hs Header is set to
Present(whenMAC-hs Headeris set toData, the transmit window size is infinite).MAC-hs Transmit Window Sizecan be set to 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, or 32. In accordance with 3GPP TS 25.321 11.6.2.3.2, the test set will not retransmit a block with a TSN that is outside the transmit window.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACHs:WSIZe:TRANsmit
-
MAC-hs HeaderYou may choose to fill the MAC-hs header with dummy data (such as PRBS, to ensure that there are no repeating patterns of data in each MAC-hs frame, or simply to provide an uninterrupted stream of PRBS data) or include a header with valid content.
PresentWhen
MAC-hs Headeris set toPresent, each MAC-hs block contains a valid MAC-hs header formatted with the following values (see 3GPP TS 25.321 9.2.2):
The TSN (Transmission Sequence Number) field is incremented each time a new block is sent by a HARQ process. When
MAC-hs Headeris set toPresent, the test set uses the MAC-hs Transmit Window Size to control its window size.-
DataWhen
MAC-hs Headeris set toPresent, the MAC-hs header space for each block is filled with FDD Test "HS-DSCH Data Pattern" data.
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACHs:HEADer .
-
FDD Test statDTX Reception Behavior
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACHs:SDTX:RBEHavior
-
FDD Test Mode statDTX Reception Behavior for Two Trans Blks
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:MACEHS:DTBLocks:SDTX:RBEHavior
HSDPA Uplink Parameters
These values are not signalled to the UE in FDD Test mode; rather, you must ensure that the UE is using the same values as these settings.
Secondary Serving Cell Parameters
- FDD Test
Dual Carrier Band Configuration
The parameter
This parameter can only be set when the
Data/Call StatusisIdle.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSDPa:MCARrier:BAND:CONFig[:TYPE]
- Secondary
Serving Cell Power
GPIB command: CALL:SSCell:POWer:AMPLitude
- FDD
Test Secondary Cell DL Channel Config
The parameter sets whether to use FDD Test Secondary Cell DL Adjacent UARFCN , or FDD Test Secondary Cell DL Manual UARFCN as the secondary serving cell downlink UARFCN when FDD Test Dual Carrier Band Configuration is set to
Single Band.This parameter can only be set when the
Data/Call StatusisIdle.GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:CHANnel:CONFig[:TYPE]
- FDD
Test Secondary Cell DL Adjacent UARFCN
When FDD Test Dual Carrier Band Configuration is set to
Single Band, and FDD Test Secondary Cell DL Channel Config is set toAdjacent, this parameter sets the downlink adjacent UARFCN of the secondary serving cell.GPIB command: CALL:SSCell:CHANnel:ADJacent
- FDD
Test Secondary Cell DL Manual UARFCN
This parameter sets the downlink manual UARFCN of the secondary serving cell when:
- FDD Test Dual
Carrier Band Configuration is set to
Single Band, and FDD Test Secondary Cell DL Channel Config is set toManual - FDD
Test Dual Carrier Band Configuration is set to
Dual BandorUser Defined
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:CHANnel:MANual:UARFcn
- FDD Test Dual
Carrier Band Configuration is set to
- FDD
Test Secondary Cell Manual Band Arbitrator
This parameter determines whether the test set sends a Band V or Band VI Frequency Band Indicator when the FDD Test Secondary Cell DL Manual UARFCN is used as the secondary serving cell's UARFCN. This setting FDD Test Secondary Cell DL Manual UARFCN is set to a value (1037, 1062, 4387 to 4413) shared by Band V and Band VI UARFCNs
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:CHANnel:MANual:BARBitrator
-
Secondary Serving Cell Primary Scrambling CodeGPIB command: CALL:SSCell:SCODe[:PRIMary] .
H-RNTI Parameters
- FDD Test Primary H-RNTI
(Hex)
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HRNTi[:PRIMary]
- FDD
Test Alternate H-RNTI (Hex)
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HRNTi:ALTernate
- FDD
Test HS-SCCH1 Alternate H-RNTI (Hex)
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HRNTi:ALTernate:HSSCCH1
- FDD
Test HS-SCCH2 Alternate H-RNTI (Hex)
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HRNTi:ALTernate:HSSCCH2
- FDD
Test HS-SCCH3 Alternate H-RNTI (Hex)
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HRNTi:ALTernate:HSSCCH3
- FDD
Test HS-SCCH4 Alternate H-RNTI (Hex)
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HRNTi:ALTernate:HSSCCH4
- FDD
Test Secondary Serving Cell H-RNTI (Hex)
GPIB command: CALL:HSDPa:SSCell:HRNTi
- FDD Test
RB Test HS-DSCH Configuration Type
-
You must set the HSDPA/HSPA DL Channel Codes (
Generator Info( F2 )>>Downlink Channel Codes( F2 ), F4 ).-
FDD Test First HS-PDSCH Channelization CodeThis parameter sets the channelization code of the first HS-PDSCH when on an FDD Test Mode connection. If more than one HS-PDSCH is being generated, the other HS-PDSCHs are assigned to the subsequent channelization codes.
This parameter cannot be set to 5 when
HSDPA DPCH 12.2k RMC Channelization Codeis set to 45 or 54, and cannot be set to 6 whenHSDPA DPCH 12.2k RMC Channelization Codeis set to 54. Also, the number of HS-PDSCHs specified by the FDD Test "FRC Type" or FDDT "User Defined Number of Active HS-PDSCHs" settings, when added to theFDD Test First HS-PDSCH Channelization Codecannot exceed 15 (otherwise the HS-PDSCHs would collide with the downlink OCNS channels).GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:HSPDschannel:CCODe
-
-
To set the downlink channel levels, you must use the HSDPA Connected DL Channel Levels settings (
Generator Info( F2 )>>Downlink Channel Levels( F3 ), F4 ).HSDPA FDD Test CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:CPIChannel[:SLEVel]:HSDPa .-
HSDPA FDD Test P-CCPCH/SCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:CCPChannel:PRIMary[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test PICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:PICHannel[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test DPCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:DPCHannel[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test HS-PDSCHs Level (Sum): CALL:FDDTest:HSPDschannel[:SLEVel] . -
HSDPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 1 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel[1][:SLEVel] . -
HSDPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 2 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel2[:SLEVel] . -
HSDPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 3 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel3[:SLEVel] . -
HSDPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 4 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel4[:SLEVel] . -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:CPIChannel[:SLEVel]:HSDPa -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell P-CCPCH/SCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:CCPChannel:PRIMary:STATe:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell PICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:PICHannel[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-PDSCHs Level(Sum): CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSPDschannel[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 1 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel1[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 2 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel2[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 3 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel3[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 4 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel4[:SLEVel]:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Antenna 2 P-CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel:LEVel:HSDPa . -
HSDPA FDD Test Antenna 2 S-CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel:SECondary:LEVel:HSDPa .
- You can vary the timing between the uplink DPCH and HS-DPCCH using the DPCH Frame Offset setting.
HSPA in FDD Test Operating Mode
This section is only applicable to the lab application or feature-licensed test application.
HSPA Activation in FDD Test
In
FDD Test operating mode, HSPA is active when
Channel Type is set to 12.2k
RMC + HSPA .
HSPA Operation in FDD Test
When HSPA is active, the test set operates a fully functional Layer1 plus MAC-e solution, in that E-DCH blocks are decoded according to the E-TFCI and the appropriate ack or nack is sent on the E-HICH. The test set discards any blocks received on the E-DCH after transmitting the ack or nack. This means that the UE may use any value it likes for the DDI, N and TSN fields in the MAC-e/es PDU. There is no signaling on the control plane above MACe/es.
While on an HSPA channel in FDD Test Mode, the HSDPA downlink operates much as it does for an HSDPA-only channel type. The primary difference is that while on an HSPA channel the HS-DSCH transmits RLC PDUs that contain valid RLC UM headers. This is in contrast to HSDPA-only FDD test mode where there are no RLC headers sent on the HS-DSCH (PRBS data is sent instead). The headers are necessary so that the UE can loop back the downlink data received on the HS-DSCH back onto the uplink E-DCH. The loopback point in HSPA FDD test mode is expected to be immediately above the UE's RLC layer (which is the same place as for active cell). This means the RLC layer must deliver complete blocks to the loopback entity for there to be data on the E-DCH. The UE's RLC UM entity can only deliver blocks up to its loopback entity if it is receiving consistent header data (not PRBS data) that allows it to recreate complete SDUs. While operating on an HSPA channel type in FDD test mode the test set therefore transmits valid RLC UM headers. The RLC PDU size is 336 bits when an HSDPA FRC is configured (this matches the specification for FRCs in 3GPP TS 34.121) or 112 bits when an HSDPA user defined configuration is used. The downlink RLC SDU size is set to 2936 bits (just like in active cell operating mode). As many RLC PDUs are packed in a single MAC-hs PDU as will fit, subject to the same limits as described in HSPA Radio Bearer Test Mode . The same MAC-hs header format as described in MAC-hs Header above is used with the exception that the N field is set to the actual number of RLC PDUs packed in the MAC-hs PDU.
To test HSPA UEs in FDD test mode, you must synchronize the UE and test set as described in Synchronizing the UE to the Test Set's Downlink to Make Measurements .
Additionally, you must consider the following:
Channel Typemust be set to12.2k RMC + HSPA( CALL:SERVice:RBTest:RAB ).- You
must ensure that you have properly configured the
HSDPA Parametersas described above in HSDPA Operation in FDD Test . -
You must ensure that you have properly configured the
HSUPA Parameters(HSPA Parameters( F10 ), F9 ): Common HSUPA Parameters , Serving Grant , E-TFCI Recording , E-RNTI Parameters andHSUPA FDD Test Mode Setup
- FDD Test
E-DPDCH Max Channel Codes
This setting is used to inform the test set (while operating in FDD Test mode) what value the UE is using for E-DPDCH Max Channelisation Codes. Knowledge of this value is necessary to be able to translate the E-TFCI value that the UE transmits on the E-DPCCH to the spreading factor and number of channels used on the E-DPDCH.
GPIB command: CALL:FDDTest:EDPDchannel:CCODes:MAX
- FDD Test
E-DPDCH Max Channel Codes
-
You must set the HSDPA/HSPA DL Channel Codes (
Generator Info( F2 )>>Downlink Channel Codes( F2 ), F4 ). See FDD Test First HS-PDSCH Channelization Code above. -
To set the downlink channel levels, you must use the HSPA Connected DL Channel Levels settings (
Generator Info( F2 )>>Downlink Channel Levels( F3 ), F5 ).HSPA FDD Test CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:CPIChannel[:SLEVel]:HSPA .-
HSPA FDD Test P-CCPCH/SCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:CCPChannel:PRIMary[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test PICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:PICHannel[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test DPCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:DPCHannel[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test E-AGCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:EAGChannel[:SLEVel] . -
HSPA FDD Test E-HICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:EHIChannel[:SLEVel] . -
HSPA FDD Test E-RGCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:ERGChannel[:SLEVel] . -
HSPA FDD Test HS-PDSCHs Level (Sum): CALL:FDDTest:HSPDschannel[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 1 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel[1][:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 2 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel2[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 3 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel3[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test HS-SCCH 4 Level: CALL:FDDTest:HSSCchannel4[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:CPIChannel:STATe:HSPA -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell P-CCPCH/SCH Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:CCPChannel:PRIMary[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell PICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:PICHannel[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-PDSCHs Level(Sum): CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSPDschannel[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 1 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel1[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 2 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel2[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 3 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel3[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Secondary Cell HS-SCCH 4 Level: CALL:FDDTest:SSCell:HSSCchannel4[:SLEVel]:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Antenna 2 P-CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel:LEVel:HSPA . -
HSPA FDD Test Antenna 2 S-CPICH Level: CALL:FDDTest:ANTenna2:CPIChannel:SECondary:LEVel:HSPA .
- You can vary the timing between the uplink DPCH and HS-DPCCH using the DPCH Frame Offset setting.