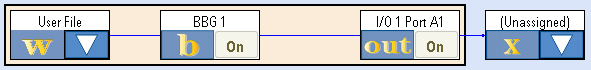

When the PXB is powered on, it displays the "1 Channel Generate" configuration, the most basic configuration in the Configuration Browser as the default. This configuration is available to all PXBs. The PXB will only display configurations that the PXB’s baseband and I/O card option structure will support.
To turn on the PXB, press the front panel power hardkey.
Allow the PXB to boot and display the firmware.
Ensure that the "1 Channel Generate" configuration is selected in the Configuration Browser.
The block diagram for this selected configuration is displayed on the Block Diagram tab.
The PXB is designed to use a variety of external instruments to provide external inputs or receive the output of the PXB. These external instruments can be controlled by the PXB firmware; however, the external instruments must be registered within the firmware prior to being available for use.
This example setup procedure uses the N5182A MXG For this example, we are calling out the Agilent MXG as the signal generator, however the Agilent E4438C ESG signal generator will also work well for the example.signal generator as the external instrument.
The registration process only needs to be performed once per instrument. If the instrument that you plan to use is already registered (see step 1 below), you may skip to the next section, "3. Assign External Instruments."
For this example, an Agilent N5182A MXG signal generator is being registered.
Click the External
Instrument Table tab to display the External Instrument Table. 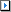
Illustration…
This illustration shows the External Instrument Table with that has been populated with several external instruments used with the PXB.
The External Instrument Table displays the external instruments that are currently registered with the PXB firmware. External instruments that can be registered are:
N5182A MXG Signal Generators (used at the output of the PXB)
E4438C ESG Signal Generators (used at the output of the PXB)
N5102A Digital Signal Interface Module (DSIM) (used at the input or output of the PXB)
N9020A MXA Signal Analyzer [used at the input of the PXB for (ext in) configurations]
The table displays the name, instrument type, address, and I/O Port (this is discussed more in the next step) of each registered external instrument. If no instruments are displayed in the table, then no instruments are currently registered.
Select the Add
button to start the registration process. This displays the Register External Instrument
dialog box.
Illustration…
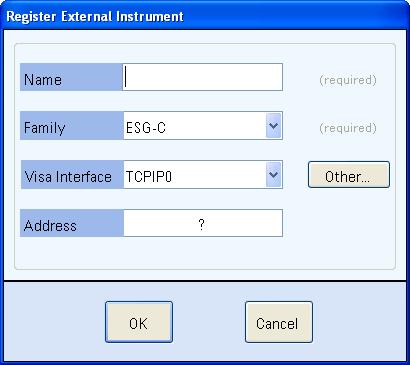
In the Name text box, enter "MXG1" or another name to describe your signal generator. For the remainder of this example, the signal generator is referred to "MXG1".
In the Family drop down list, select instrument family that describes the instrument's family. In this case, select MXG.
In the Visa Interface drop down list, select the interface that the PXB will use to communicate with the instrument (TCPIP0 = LAN or GPIB0 = GPIB).
In the Address text box, enter the address specific to the instrument that you are registering.
| As you proceed through this step, use the actual addresses for your instruments. |
Click the OK button to complete the registration. The External Instrument Table should now show the instrument that you just registered (an MXG, in this case).
Click the Block Diagram tab to return to the configuration block diagram that was originally displayed.
External instruments must be selected and set up for the PXB.
In the Configuration Browser, ensure that the Generate 1 Channel configuration is selected.
Review the block diagram.
You will see a User File block, a BBG 1 block and an I/O1 Port A1 block (this block is an output which connects to a signal generator). You will also see an (Unassigned) block which represents an unassigned block for an external instrument (the signal generator).
In the unassigned external instrument block, click
the ![]() button to
display the Assign
External Instrument dialog box.
button to
display the Assign
External Instrument dialog box.
In the Assign
area of the Assign External Instrument
dialog box, select the MXG signal generator that you previously registered.
Illustration…
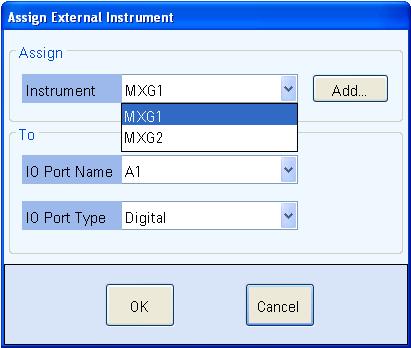
In the To area, leave the I/O Port Name field set to the default selection. Ensure I/O Port Type field is set to Digital.
The I/O Port Name field allows you to select any available I/O port.
The I/O Port Type field allows you to select from two types of I/O port connections, digital or analog, for the ESG or MXG signal generators. For additional information, refer to Assign External Instrument.
Click OK to return to the block diagram. Note that the external instrument block now displays the selected signal generator.
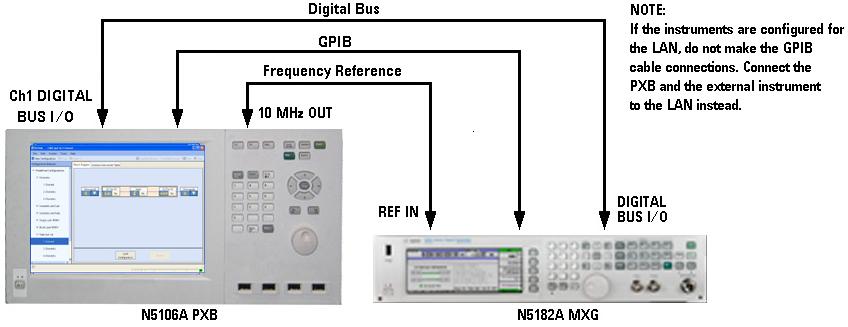
Connect the PXB to the signal generator as shown.
Illustration…
Waveform (User File) blocks enable the user to select the signal creation source from an arbitrary waveform file (User File) or from a Signal Studio real-time option. In this example, we will select an arbitrary waveform file.
In the waveform block, click the ![]() button to display the
button to display the  Assign
Waveform Source
dialog box.
Assign
Waveform Source
dialog box.
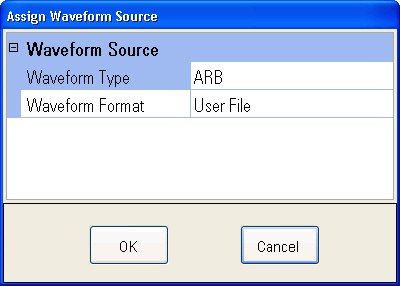
Select ARB as the waveform type and User File as the waveform format.
Click OK to return to the block diagram. Note that the external instrument block now displays the selected signal generator.
Select the Load Configuration button to load the settings for each of the configuration blocks.
When the configuration is loaded, the Settings Browser replaces the Configuration Browser in the left panel of the user interface. Each block from the block diagram is also listed in the Settings Browser. You are now able to view and edit the settings for each block.
Set up the waveform and baseband generator blocks, and download an example waveform to play.
Open the waveform settings for User File1. This can be done in one of two ways:
Select the User File1 block in the block diagram
Select the User File1 label in the Settings Browser
Select Waveform
Source Name to display the ellipsis ![]() button at the right edge of its settings cell. Then
select the ellipsis button to display the Open
File dialog box.
button at the right edge of its settings cell. Then
select the ellipsis button to display the Open
File dialog box.
For this example, ensure the "Default1.bin" waveform is selected. (you will download it to baseband generator memory in a later step)
The default folder, C:\<Program Files for Win XP><Program Files (x86) for Win 7>\Agilent\PXB\FactoryDefaultWaveforms, contains several factory default waveforms. Refer to Factory Default Waveform Files for a description of these waveforms.
If you have already loaded other waveform files on the PXB, you can navigate to the folder it was saved in using the Open File dialog box.
In the Settings Browser or the block diagram, open the baseband generator settings for BBG 1.
Notice the four tabs that are displayed: General
Settings, Marker Generation,
Power Calibration Settings, and
Power Calibration Graphics
Illustration…
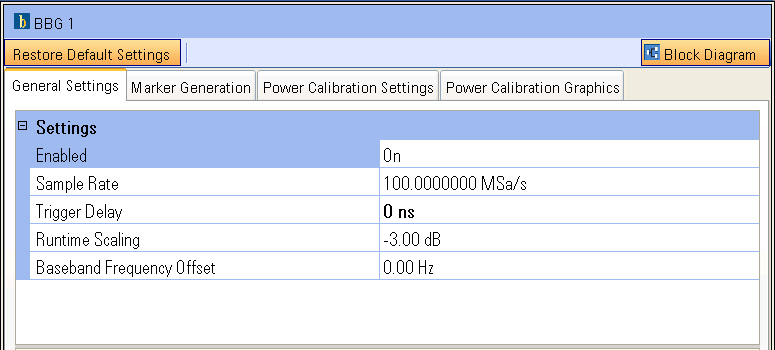
Selecting a tab label displays the tab’s settings. The General Settings are similar to those found in traditional signal generators, such as Sample Rate, Trigger Delay, and Baseband Frequency Offset, allowing you to have a frequency offset in the baseband which offsets the carrier from the signal frequency.
Select the Marker Generation tab to review this tab's settings. You may refer to the Marker Basics tutorial for additional information regarding markers.
Select the Power Calibration Settings tab to review this tab's settings. The Power Calibration Graphics tab provides a graphical description of some of the power control settings. You may also refer to the Power Management and AWGN tutorial for additional information regarding power control.
Select the Block Diagram button to return to the block diagram.
Select the Download Panel button to display the Download table.
The table displays the selected waveform source file as Waveform 1. Notice that Waveform Status is ”Out-of-Date” and Download Status is ”Not Started,” which indicates that the waveform has not been loaded to the baseband generator yet.
Select the Start button to download the designated waveform from the PXB hard drive to the playback memory of the baseband generator.
Notice that, once the waveform has been downloaded, Waveform Status is displayed as ”Up-to-Date” and Download Status is displayed as ”Completed.”
Return to the block diagram.
The output I/O port is used as the output interface to an external instrument (either a signal generator or an N5102A Digital Signal Interface Module) at the output of the PXB. the output I/O Block has its own settings that are customized for the output. For additional information, refer to the I/O Port Setup tutorial.
Open the I/O Port settings for I/O1 Port A1. This can be done in one of two ways:
Select the I/O1 Port A1 block in the block diagram
Select the I/O1 Port A1 label in the Settings Browser
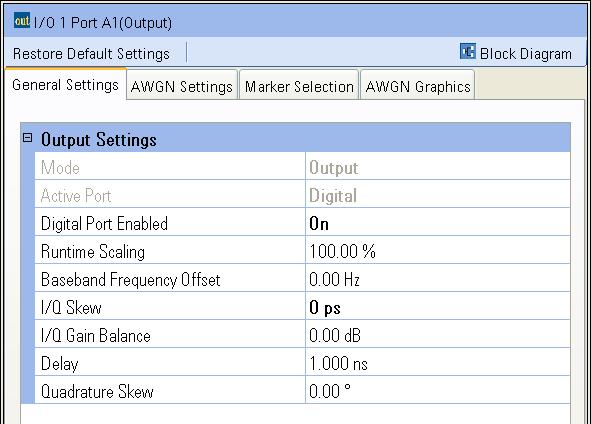
Notice the four tabs that are displayed: General
Settings, AWGN Settings,
Marker Selection, and AWGN
Graphics.
Illustration…
The following is a quick review of how each of the tabs can influence the output of the PXB.
Review the General Settings tab.
The General Settings tab provides information about the I/O port and can be used to make changes to the I/O port. You will notice that the Mode setting is a read-only entry that displays Output indicating that this I/O port is being used as an output I/O.
Select the AWGN Settings tab to review this tab's settings. This tab is used to add and control Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) to the output signal at the I/O port. The AWGN Graphics tab provides a graphical description of some of the AWGN settings.
Select the Marker Settings tab to review this tab's settings. For additional information, you may also refer to the Marker Basics tutorial.
The I/O output block can pass the existing markers from the input source (the baseband generator or I/O input block) or can dynamically generate new markers based on the waveform present at the I/O output block. Markers that are generated from an output I/O block that is receiving a single-input waveform are merged with the waveform as it was received. Therefore, if the original waveform has had fading or interference added, the degraded waveform is used to generate these markers. This is important to note because dynamic markers use the values of the waveform samples to determine when markers are generated.
Any output I/O markers will override markers previously embedded in the original waveform file or generated by a user-created marker file or baseband generator block.
Return to the block diagram.
The PXB provides direct control of several of the signal generator settings. These settings include the output frequency, the output amplitude, and the internal marker routing and more. It does not provide control of all the signal generator settings.
Open the MXG settings for MXG1, the signal generator that we have assigned as the external instrument for this configuration. This can be done in one of two ways:
Select the MXG1 block in the block diagram
Select the MXG1 label in the Settings Browser
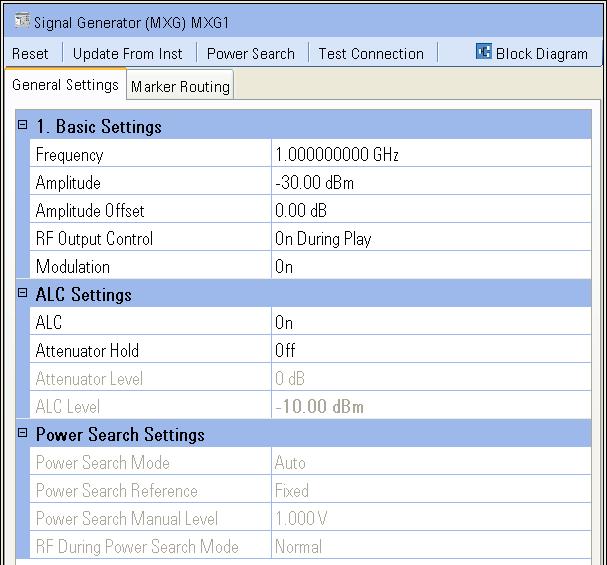
Notice that
this external instrument has two tabs that are displayed: General
Settings and Marker Routing
Illustration…
Select the Preset button to preset the signal generator.
Review the General Settings tab.
The General Settings tab
is comprised of three categories:
Basic Settings which provides control of very basic signal generator settings.
ALC Settings which provides control of the signal generator’s Automatic Level Control (ALC) and attenuator circuitry.
Power Search Settings which provides control of the signal generator’s power search function when a power calibration is performed.
Set the RF Output parameter to On so the signal generator’s RF Output connector will be on when the waveform is played.
Set the ALC parameter to Off so the signal generator’s ALC circuitry will not interfere with the power calibration when it is performed.
Select the Marker Routing tab to review this tab's settings. This tab allows you to set up the markers to control the Pulse/RF Blanking and the ALC Hold features. For additional information, you may also refer to the Marker Basics tutorial.
Return to the block diagram.
Once the PXB configuration is set to meet your test needs, you can simply calibrate the system power and play the waveform from the BBG 1 block through the I/O block to the connected signal generator via the digital bus.
Power calibration occurs automatically by default. If
you want manual control of power calibration, select Maunal
in the System > Calibration > Power
Calibration menu, then select the Calibrate
Power button to perform the power calibration based on the baseband
generator block's Power Control Settings and the output I/O block's AWGN
Settings.
More information
| You cannot perform a Calibrate Power operation unless the selected waveform in the Download Panel has both "Up-to-Date" and "Completed" waveform status. |
Select the Play button to start playing the waveform from BB Gen1.
When you wish to stop playing the waveform, select the Stop button.
To save the configuration and its settings, select Save from the File menu.
To recall the configuration and its settings, select Recall from the File menu.