Probes
The N1021B TDR/TDT probe is available for use with the N1000A.
For limited support for legacy DCA plug-in modules using compatible probes, install FlexDCA revision A.07.90 and below.
N1021B 18 GHz Differential TDR/TDT Probe Kit
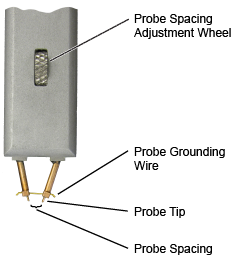
The N1021B TDR/TDT probe kit includes the N1021-60001 TDR/TDT probe which facilitates differential time domain reflectometry measurements in situations where RF connectors are unavailable. It is ideal for use with the Keysight N1055A TDR plug-in module. Although the N1021B probe was designed for TDR applications, it is also suitable as a high bandwidth, passive probe for non-TDR applications. The spacing between the probe's tips can be adjusted by turning the probe spacing adjustment wheel.

Using the adjustment wheel, you can adjust the spacing between the two probe tips.