:SPRocess:RMODel:PNOise
Command Syntax
:SPRocessN:RMODel:PNOise {NONE | PRMS | SPECtrum}
Where N identifies one of up to 64 possible operators {1:64} that can be defined as part of a math function. The operators are numbered in the order that they were originally added to the function.
Query Syntax
:SPRocess:RMODel:PNOise?
Description
 Selects to preserve noise of a Rx Model filter operator. If a status message indicates that the output is questionable due to "The source waveform has not been acquired with enough samples per symbol to accurately represent noise", increase the samples-per-bit setting as explained for the
Selects to preserve noise of a Rx Model filter operator. If a status message indicates that the output is questionable due to "The source waveform has not been acquired with enough samples per symbol to accurately represent noise", increase the samples-per-bit setting as explained for the :ACQuire:SPUI:MODE command.
Command arguments:
NONE. Noise handling is turned off.PRMS. Applies preserve RMS noise handling where the noise magnitude is kept the same as the channel.SPECtrum. Applies process spectrum noise handling where the function increases or decreases the noise based on whether SIRC is increasing or decreasing bandwidth. The noise power spectrum is assumed to match the channel response.
Turning preserve noise on compensates for the filter function's side effect of reducing a signals noise for adjacent measurement points. Preserving noise causes the operator to quantify the noise on each point on the operator's input waveform and restore this noise on the corresponding data point on the output waveform. Because this increases the fidelity of the waveform, it is recommended that preserve noise be used. An example of an advantage of using this feature is during Mask testing, as without preserving the noise the mask hits counts may be too low (optimistic).
By default, the bandwidth used when preserving the noise is automatically used. To manually set the bandwidth, use the :BANDwidth child command to enter the value and set the :BANDwidth:AUTO child command to OFF.
NONE Argument
The option NONE
SPECtrum Argument
The option SPECtrum
The default behavior of the Process Spectrum noise processing option is to use the noise power spectrum of the input signal. If the input signal is a sampling scope channel with SIRC active, this spectrum will be established by the measured hardware response of the channel. For other channels, the response will be assumed Gaussian with a 3 dB frequency corresponding to the nominal channel bandwidth. This behavior can be overridden by clearing the Track Input Response checkbox and manually entering a bandwidth. If this option is utilized the response will be presumed Gaussian with the selected 3 dB bandwidth.
PRMS Argument
The option PRMS
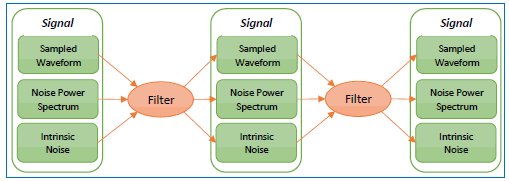
By tracking the accumulated effects of the filtering operations, accurate noise processing can be done even when chaining operations as illustrated in the following figure. In addition to the sampled waveform, information about the acquisition channel and noise power spectrum are maintained in each signal and appropriately processed by each filter. The complete set of auxiliary information is also included when storing FlexDCA waveforms in the *.wfmx file format.
Requires FlexDCA revision A.07.80 or greater.