How to make SMC or VMC settings
To provide quicker access, use the Setup softkey. Learn how.
Using front-panel
hardkey [softkey] buttons
Using Menus
-
Press Freq
-
then [Mixer Setup]
-
Click Stimulus
-
then Freq
-
then Mixer Setup
FCA includes both Scalar (SMC) and Vector (VMC) measurements and calibrations.
In this topic:
For a detailed understanding of FCA, see our Mixer Measurements App Notes.
What's new in FCARev A.09.33 |
Option 083 provides FCA which includes Scalar Mixer (SMC) and Vector Mixer (VMC) Measurements.
Option 082 provides ONLY SMC measurements. This is the ONLY FCA option that is allowed on the N5230C.
Option 084 provides Embedded LO measurements. This option requires one of the Converter Applications.
|
|
Scalar Mixer Calibration |
Vector Mixer Calibration |
|
Overview |
Provides highest Scalar accuracy for measurements of conversion loss/gain. Combines SOLT and power-meter calibration. Simpler setup than Vector Mixer Calibration. |
Provides unparalleled accuracy for measurements of relative phase and absolute group delay. Uses combination of SOLT standards and a reciprocal mixer/filter pair during calibration. More complicated setup and calibration procedure than Scalar Mixer Calibration. After calibration, both reciprocal and non-reciprocal mixers and converters can easily be measured. |
|
Measurements Offered |
Both forward and reverse directions. DUT can be connected to any VNA ports. |
Amplitude response VC21 Phase response Group delay DUT input must be connected to PNA port 1. DUT output can be connected to any other PNA port. |
|
Equipment Required |
Power meter and sensor |
Calibration mixer/filter combination (must be reciprocal S21 = S12.) |
|
Common equipment for both SMC and VMC
|
||
See Comparison of Mixer Characterization using New Vector Characterization Techniques.
The following VNA features are NOT available with FCA:
Analog Sweep (Stepped sweep mode only)
Log frequency sweeps
ECal User Characterization (can NOT be created in FCA channel)
External Test Set Control (Option 551)
The following is an overview of how to make an FCA measurement:
DECIDE to use either a SMC or VMC measurement. See a comparison of these two measurement types.
CREATE an SMC or VMC Measurement.
SETUP the measurements.
CALIBRATE your SMC or VMC measurement.
Press Meas then [Measurement Class]
Select SMC or VMC, then either:
OK delete the existing measurement, or
New Channel to create the measurement in a new channel.
The default SMC or VMC measurement parameter is displayed.
See SMC measurements or VMC measurements to learn about the parameters that are offered in each.
How to make SMC or VMC settingsTo provide quicker access, use the Setup softkey. Learn how. |
|
|
Using front-panel |
Using Menus |
|
|
Configuring the SMC and VMC Setup dialog can be challenging at first. RED messages like this one appear at the bottom of the Setup dialog to notify you of an invalid setup.
![]()
At least one range (Input, LO, or Output) MUST be Fixed.
The following are the Valid Mixer Configurations:
|
Sweep Type |
Input |
LO |
Output |
|
Linear |
Swept |
Swept |
Fixed |
|
Swept |
Fixed |
Swept |
|
|
Fixed |
Swept |
Swept |
|
|
CW Time Power |
Fixed |
Fixed |
Fixed |
TipsAlthough you will soon become comfortable navigating these tabs, at first it may be best to complete the dialog in the following order:
|
The following FCA settings are common to VMC and SMC:
|
Sweep TypeLinear Sweep frequency. Measurements are displayed on a standard grid with ten equal horizontal divisions. Learn how to select the range to display on the X-Axis. CW Time All ranges are set to a Fixed (CW) frequency, and the data is displayed versus time. Segment Sweep Sweep user-defined segments. Learn more. Power Sweep Input or LO power.
X-axis Point Spacing (Available only with Segment Sweep) - Learn about this feature Avoid Spurs - Learn about this feature. Reversed Port 2 Coupler (SMC ONLY) Check when making SMC measurements with the Port 2 coupler reversed. Learn how. Do this to increase power at low frequencies. Checking this box has the following effects:
Number of Points Learn about this feature. IF Bandwidth Learn about this feature. Phase Reference Point (SMC ONLY) Learn about this feature.
|
|
Note: Set LO Power on the Mixer (LO) Power tab.
Configures Input and Output power settings for an FCA measurement. Use the Mixer Power tab to set LO power. Power ON (All channels) Check to turn RF Power ON or clear to turn power OFF for all channels. Port Powers Coupled Check to set the same power level at the DUT Input and Output ports. The LO power is NOT coupled. Clear to set power levels independently for each test port. Uncouple power, for example, to apply more power in the reverse direction than in the forward direction Learn more about Setting Independent Port Power DUT Input / Output PortSelect the port that is connected to the DUT Input and Output. For VMC, the DUT input must always be connected to PNA port 1 because of the need for a reference mixer on port 1. Power Level Set the power level to the DUT Input port. To set power at the Output port, clear the Port Powers Coupled checkbox. Source Attenuator Auto Check to automatically select the correct attenuation to achieve the specified input power. Clear, then select attenuator setting that is used achieve the specified Power Level. Learn more about Source Attenuation. All PNA channels in continuous sweep must have the same attenuation value. Learn more. Receiver Attenuator Specifies the receiver attenuator setting for the DUT port. Source Leveling Mode Choose from: Internal (normal operation), Open Loop (used only for Wideband Pulse measurements), or Receiver - R1 for Receiver Leveling. DUT Input and Output Port Power SweepAvailable when Power (sweep) is selected on the Sweep tab. Input Start and Stop Power To set Start and Stop power at the Output port, clear the Port Powers Coupled checkbox. Note: If your DUT requires more input power than this setting allows below 3.2 GHz, use the PNA-X Hi-power mode, available from the RF Path Configuration dialog. The disadvantage to this is higher harmonic content. Power Points Number of power points to measure. Power Step (Size) Calculated value from current Start, Stop, and Points settings. This setting can NOT be changed directly. Path Configuration click to launch the RF Path Configuration dialog.
|
The following tabs are shared with all Mixer / Converter Applications:
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following settings appear on the Mixer Frequency tab when Segment Sweep is selected on the Sweep tab.
|
Mixer Frequency tab - Segment Sweep - SMC and VMC dialog box help |
|
How to configure a segment:
|
In general, when a Cal Set covers a wider frequency range than the channel, the PNA will offer to interpolate the Cal Set when it is applied. Learn more. However, with FCA measurements the LO frequency range may also be considered.
VMC measurements ALWAYS CONSIDER the LO frequency range and performs interpolation if possible. If the LO frequency range of the measurement is NOT within the LO frequency range of the Cal Set, than the Cal Set can NOT be applied.
SMC measurements ALWAYS IGNORE the LO frequency range. Therefore, if the Input and Output frequency ranges of the measurements are within those of the Cal Set, then the Cal Set is interpolated if necessary and applied. For example, this would allow you to perform ONE SMC calibration with Input range = the PNA frequency span, LO at 0 Hz, and Output range + the PNA frequency span. This Cal Set could be applied to ALL SMC measurements. Learn more about applying SMC al Sets.
These same general concepts apply to segment sweeps. However, if ALL applicable frequency ranges (SMC: Input and Output and VMC: Input, Output, and LO) are NOT within those ranges of the measurement for ONE segment, then the Cal Set is NOT applied for ANY segment.
Click Response, then Measure, then Select X-axis, then Input, LO, or Output
When Sweep Type = Linear, you can choose to show the frequency range of any of the swept parameters on the X-axis.
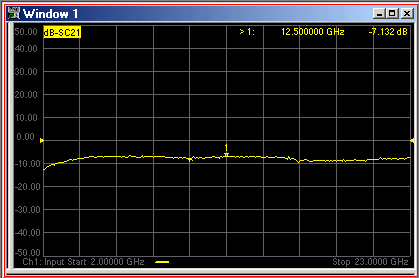
For example, the following image shows an SMC Fixed Output response with the Input frequency range on the X-axis:
Output: 100 MHz (data trace)
Input: 2 GHz to 23 GHz (X-axis)
LO: 1.9 GHz to 22.9 GHz (not shown)
Marker annotation shows Output power at Input frequency.
You can save your FCA measurement data in several standard formats.
Click File, then Save Data As to save your FCA data.
The following shows how CSV and SNP files are saved.
When you select Mixer Trace Data, the FCA data is saved to a CSV file in the following format:
#MIXER TRACE FILE,A.01.00
SegIndex, InputFreq, OutputFreq, LO1Freq, InputPower, LO1Power, SC21 Mag (dB), SC21 Phase (Deg)
Each record contains 1 stimulus value and 4 parameters (total of 9 values) as follows:
Stim Real(p1) Imag(p1) Real(p2) Imag(p2) Real(p3) Imag(p3) Real(p4) Imag(p4)
where pX is the parameter depending on measurement type:
|
Measurement Type |
p1 |
p2 |
p3 |
p4 |
|
Scalar |
S11 |
SC21 (FWD) |
SC12 (REV) |
S22 |
|
Vector |
S11 |
VC21 |
VC12 |
S22 |
|
Mixer Characterization |
Directivity |
Source Match |
Reflection Tracking |
M21 |
If correction is OFF, data is only saved for the active parameter. Zeros are saved for all other parameters.
If correction is ON, data is saved for all of the parameters.
All files contain the following Header Information: Brackets [ ] contain parameters.
!Keysight [Instrument Model Number]: [version]
!Mixer S2P File: [Mixer Measurement Type]
!Parameters: [Parameter List]
!Calibration State: [On/Off]
!# Begin Mixer Setup
![Mixer Setup parameters listed here]
![Mixer Parameter 1]
.
.
![Mixer Parameter n]
!# End Mixer Setup
# [S2P data here]
On the Mixer Setup dialog box, check Avoid Spurs
The Avoid Spurs feature of the Frequency Converter Application attempts to prevent unwanted mixing products from appearing on the PNA screen. The Avoid Spurs feature does not significantly impact measurement speed.
Note: The Avoid Spurs feature is OFF by default for FCA calibrations. For highest accuracy, make measurements with the Avoid Spurs feature at the same state (ON or OFF) as was used when calibrating.
A spur, or spurious signal, is a term used to describe the unwanted product of two signals mixing together. When you configure the mixer setup dialog box for a desired Output, the PNA computes the frequencies of potential unwanted signals. By manipulating internal PNA hardware, these signals are avoided and do not appear on the PNA display. This means you do not need to use external filters to prevent spurious signals from appearing on the PNA display.
The time required for the PNA to compute the frequencies of unwanted spurious signals MAY be noticeable depending on the number of data points in your measurement. However, once computed, the time required for the PNA to avoid the spurs is usually insignificant.
The Avoid Spurs utility cannot avoid every spur. However, when there is a choice of spurs to avoid, it will avoid the largest spur.
The Avoid Spur computer avoids the following spurs:
LO, and its interaction with internal PNA components, and 16 of its harmonics.
Input frequencies and 16 of its harmonics.
Undesired Image frequencies (Sum or Difference) and 16 of its harmonics.