Jitter Mode Setup (Advanced tab)
Advanced with RJ/RN Stabilization
Use the Advanced tab of the Jitter Mode Measurements Setup dialog, to configure advanced jitter mode settings. In this picture, click on the Separation Method, Stabilization and RJ/RN Compensation tabs to learn more.
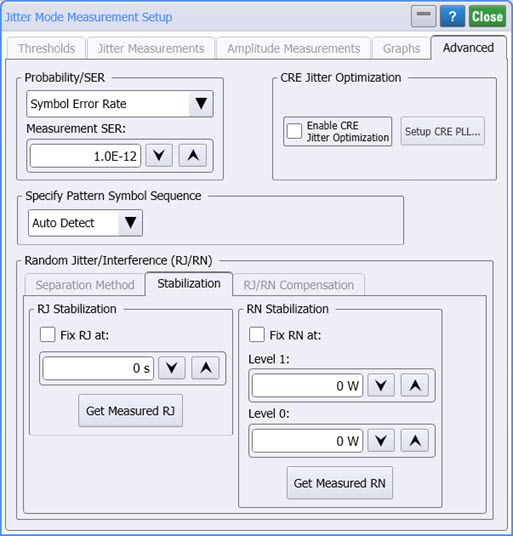
Probability/SER
Use to specify PAM4 jitter analysis to be based on probability or Symbol Error Ratio (SER). TJ, TI, eye width, and eye height measurements in the latest standards are made at probabilities instead of SER.
CRE Jitter Optimization

If JSA is available, the CRE Jitter Optimization field will be displayed. Select Enable CRE Jitter Optimization to apply clock-recovery emulation to Jitter Mode's RJ measurement. This feature is only available if JSA is turned on in Jitter mode and the JSA spectrum is set for Embedded. You can also apply jitter optimization by clicking the CRE Jitter Optimize button that is located on the JSA/CRE toolbar. Click the Setup CRE PLL button to configure the clock-recovery PLL emulation.
CRE Jitter Optimization is only available if an N1060A or 86108A/B Option JSA module is installed in the DCA-X. Installing this module makes available Jitter Spectrum Analysis on FlexDCA.
Specify Pattern Symbol Sequence
Use this setting to specify the input waveform's pattern symbol sequence (NRZ or PAM4). As shown in the following picture, you can select to have the pattern automatically detected (default), select from a standard Known Pattern, or import a BERT Pattern File (*.ptrn). Available known patterns are listed in the following table. If you select to import a PAM4 Pattern File, you should indicate if the pattern uses Gray Coding. Gray coding, or reflected binary code, is a coding pattern where successive symbols differ by one binary bit. For example in the case of PAM4, binary bit sequences 00, 01,10, and 11 represent levels 0, 1, 2, and 3.
Pattern Length Selections
Availability of individual patterns depends on installed modules and other conditions.
- 20 - 2˄7-1 PRBS
- 40 - PCIe Compliance
- 62 - PAM4 Clock
- 120 - FC RPAT
- 160 - PAM4 Linearity
- 384 - 802.3ae TWDP segment
- 640 - PCIe Idle
- 1280 - FDDI Jitter
- 2280 - CRPAT
- 2640 - CJPAT
- 3360 - CRPAT (2)
- 3760 - CJPAT (2)
- 3780 - XAUI CRPAT
- 3820 - XAUE CJPAT
- 5280 - GbE Test Frame
- 7641 - XAUI CJPAT
- 9000 - JTPAT
- 18944 - CEI Stress
- 20480 - SPAT
- 20840 - CSPAT
- 21760 - CJTPAT
- 30240 - XAUI CRPAT
- 32762 - CEI SSPR
- 33792 - 10GbE
- 65535 - SSPRQ
- 90000 - FDDI Wander
- 92160 - SATA
- 311040 - SONET CID
- 127 - 2˄7-1 PRBS
- 128 - 2˄7 PRBS
- 511 - 2˄9-1 PRBS
- 512 - 2˄9 PRBS
- 1023 - 2˄10-1 PRBS
- 1024 - 2˄10 PRBS
- 2047 - 2˄11-1 PRBS
- 2048 - 2˄11 PRBS
- 8191 - 2˄13-1 PRBS
- 8192 - 2˄13 PRBS
- 32767 - 2˄15-1 PRBS
- 32768 - 2˄15 PRBS
- 65535 - 2˄16-1 PRBS
- 65536 - 2˄16 PRBS
- 1048575 - 2˄20-1 PRBS
- 1048576 - 2˄20 PRBS
- 8388607 - 2˄23-1 PRBS
- 8388608 - 2˄23 PRBS
Stabilization Tab
The Stabilization tab does not apply to 12-Edge Output Jitter measurements.
RJ Stabilization
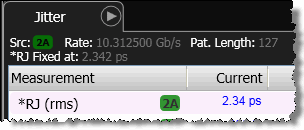 Select Fix RJ at to lock (stabilize) the value of the measured RJ that is used in jitter measurements. RJ stabilization prevents any uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic jitter from falsely contributing to any measured RJ value. One use of RJ stabilization is to prevent cross talk, from an adjacent channel, appearing as jitter. When stabilization is on, the measurement pane shows an asterisk is shown next to the RJ (rms) measurement results warning you that the measurement result has been modified. Above the panel the annotation *RJ Fixed at: lists the entered value.
Select Fix RJ at to lock (stabilize) the value of the measured RJ that is used in jitter measurements. RJ stabilization prevents any uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic jitter from falsely contributing to any measured RJ value. One use of RJ stabilization is to prevent cross talk, from an adjacent channel, appearing as jitter. When stabilization is on, the measurement pane shows an asterisk is shown next to the RJ (rms) measurement results warning you that the measurement result has been modified. Above the panel the annotation *RJ Fixed at: lists the entered value.
Click Get Measured RJ to automatically enter the current measured RJ value. This RJ value will be locked in subsequent jitter measurements.
To manually enter the RJ value, perform the following steps:
- Remove any sources of uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic jitter (for example, cross talk or non-periodic electromagnetic interference).
- Unselect Fix RJ at, measure the RJ, and enter the measured RJ into the Fix RJ at field.
- Turn RJ stabilization on and reapply the sources of uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic jitter.
RN Stabilization
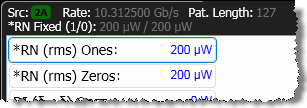 Select Fix RN at to lock (stabilize) the value of the measured RN that is used in amplitude measurements. RN stabilization to prevent any uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic amplitude noise from falsely contributing to any measured RN value. One use of RN stabilization is to prevent cross talk, from an adjacent channel, appearing as noise. When stabilization is on, the measurement pane shows an asterisk is shown next to the RN (rms) measurment results warning you that the measurement result has been modified. Above the panel the annotation *RN Fixed (1/0): lists the entered values. Enter RN one/zero values in volts (electrical) or watts (optical), depending on the type of signal that you are measuring.
Select Fix RN at to lock (stabilize) the value of the measured RN that is used in amplitude measurements. RN stabilization to prevent any uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic amplitude noise from falsely contributing to any measured RN value. One use of RN stabilization is to prevent cross talk, from an adjacent channel, appearing as noise. When stabilization is on, the measurement pane shows an asterisk is shown next to the RN (rms) measurment results warning you that the measurement result has been modified. Above the panel the annotation *RN Fixed (1/0): lists the entered values. Enter RN one/zero values in volts (electrical) or watts (optical), depending on the type of signal that you are measuring.
Click Get Measured RN to automatically enter the current measured RN value. This RN value will be locked in subsequent amplitude measurements.
To manually enter the RN value, perform the following steps:
- Remove any sources of uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic noise (for example, cross talk or non-periodic electromagnetic interference).
- Unselect Fix RN at, measure the RN, and enter the measured RN into the Fix RN at field.
- Turn RN stabilization on and reapply the sources of uncorrelated non-Gaussian, non-periodic noise.