Mask Test Margins
Use the Mask Test Margins dialog to specify the compliance margin for a standard or scaled mask. (Click Measure > Eye/Mask Mode > Mask Test Margins.) Margins indicate areas that are to contain a specified number of hits (violations within the mask region) in order to comply with testing standards. You can use this information to determine at what level the waveform begins to fail to comply with industry standards.
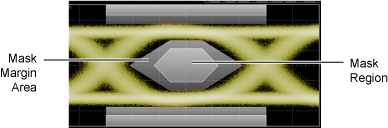
Once you have defined your margins, select Mask Test Margins On to apply your margins. Mask regions are shown in light gray and mask margins are shown in dark gray. Any acquired data point that falls inside a mask margin appears in red.
Margin Type: Auto
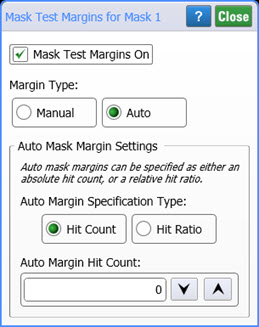
In the Margin Type field, select Auto to automatically set the mask margins based on your entered target Hit Count or target Hit Ratio. Selecting Hit Count sets the margins so that:
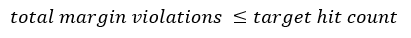
Selecting Hit Ratio causes the margins to be sized to achieve the entered Auto Margin Hit Ratio. Use Hit Ratio based mask testing with measurement limit testing (based on percent uncertainty) to reduce test times while increasing test repeatability. This is especially important in testing high-volume optical transceivers. Click on the following link to discover how Hit Ratio based mask testing works. Use the following procedure to set up your testing.
Running a Hit-Ratio based mask-margin test
- Click Measure > Eye/Mask Mode > Mask Test Margins to open the Mask Test Margins dialog.
- In the Margin Type field, select Auto.
- Select Hit Ratio as the Auto Mask Margin Settings and enter the desired Auto Margin Hit Ratio. Typically this is 5.0E−5 (allows 1 violation in every 20000 samples).
- Close the dialog.
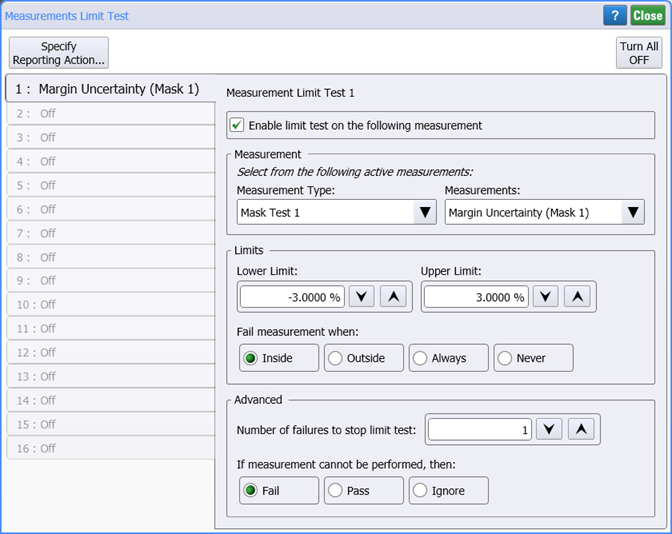
- Click Measure > Limit Tests > Measurement Limits to open the Measurement Limit Test dialog.
- In the dialog, click Turn All Off.
- In the Available Measurements field, select Margin Uncertainty. Enter the remaining settings as shown in the following figure. Set the Lower Limit and Upper Limit to set the percentage range of margin uncertainty that you want to stop the mask margin testing. In this picture, ±3% is entered. When the uncertainty drops within this limit, the testing stops.
- Close the dialog.
- Click Stop/Single on the menu bar to stop data acquisition.
- Click Clear on the menu bar to clear the display.
- Click Run on the menu bar to run the test.
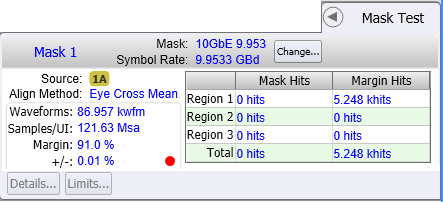
- When the limit test completes, in the Mask Test results panel you'll notice that a red dot is shown next to the +/− entry. This entry shows the uncertainty percentage that stopped the testing. Notice also that in this case 338,670 samples were acquired. Increasing the test limits will shorter the test times.
Margin Type: Manual
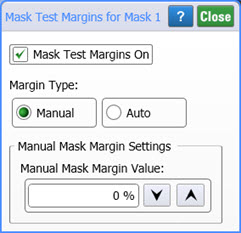
When Manual Margin Type is selected, you can specify positive or, negative mask margins:
- Positive margins (0% to +100%) determine how much larger you will be able to increase the mask size before violations occur.
- Negative margins (0% to −100%) determine how much smaller you have to decrease the mask size before violations no longer occur.
The margin percent setting is determined according to the following equation: violations = BER (samples/UI)
where UI is the unit interval.
The following pictures give examples of positive and negative margins used to verify that the waveform can comply to a standard mask with a 20% margin. You can then increase the size of the margin by increasing the percentage until violations occur. Margin and standard mask violation counts appear on the Mask Test results table.
Positive Mask Margins (+20% margin)
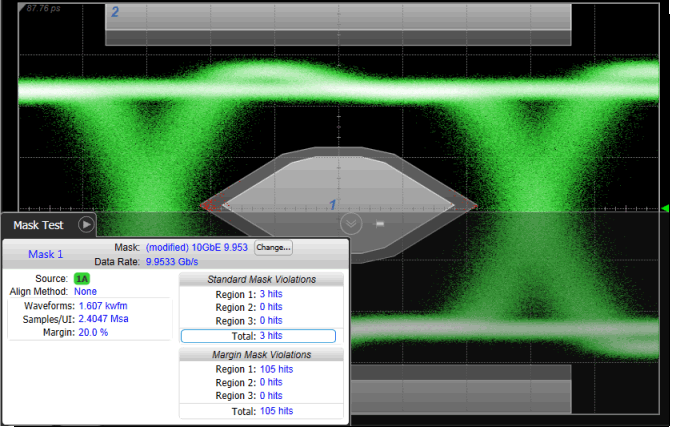
For positive mask margins:
- Total Standard Mask Violations show the number of data points sampled in the mask regions (mask failures). This count does not include any point within the margin area
- Total Margin Mask Violations show the number of data points sampled in the mask margin regions (margin failures). This count does include any point within the standard mask area.
Negative Mask Margins appear inside the mask regions. (–20% margin)
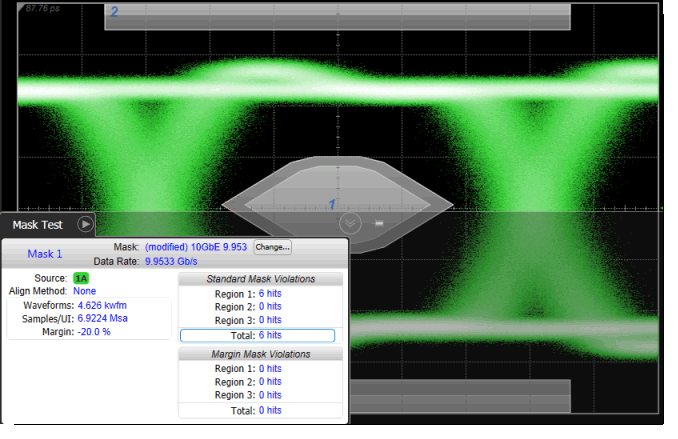
For negative mask margins:
- Total Standard Mask Violations show the combined number of data points sampled in the mask regions and mask margin regions (mask failures). This count does include points within the margin area.
- Total Margin Mask Violations show the number of data points sampled in the mask margin regions (margin failures). This count only includes points within the margin but not outside the margin area into the standard mask area.