Noise Margin (rms)
 The Noise Margin (rms) measurement measures the electrical output of an O/E receiver. This is a single measurement that includes the contribution of all three PAM4 waveform eyes. This differs from a Partial Noise Margin measurement where three individual noise-margin measurements with each measurement based on the contribution of a single PAM4 eye.
The Noise Margin (rms) measurement measures the electrical output of an O/E receiver. This is a single measurement that includes the contribution of all three PAM4 waveform eyes. This differs from a Partial Noise Margin measurement where three individual noise-margin measurements with each measurement based on the contribution of a single PAM4 eye.
This measurement can only be performed on a PAM4 waveform.
Requires pattern lock.
Noise margin is a system-level test that measures the amount of noise power that can be added to a system while maintaining its performance at a specific Symbol Error Ratio (SER) at the output of an O/E receiver. This differs from a TDECQ measurement which is performed at a transmitter's output and is not a system-level test. TDECQ is unsuitable for a system-level test due to the expectation that TDECQ remain constant if overall optical power and OMA is reduced in a linear method.
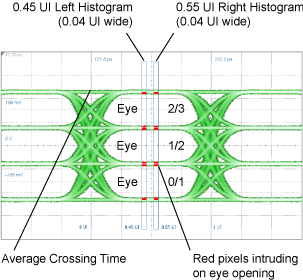
Like the TDECQ measurement, the Noise Margin (rms) measurement is made using two vertical histograms which are located at 0.45 UI and 0.55 UI from the waveform's average crossing time. The location of these histograms is annotated on the displayed waveform. This location of the histograms ar shown in the following figure. The red pixels areas on the top and bottom eye edges highlight the areas that contribute the most to poor TDECQ results. The more equally spaced the red pixel areas are, the more distributed the errors.
Additional Insights
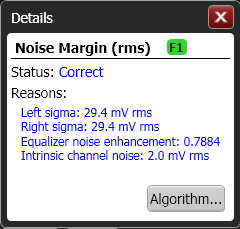
Click the Details button that is shown in the Results panel for supplemental measurement information as shown in the following picture. This information can also be returned programmatically by using the :MEASure:EYE:NMARgin:STATus:DETails? query.